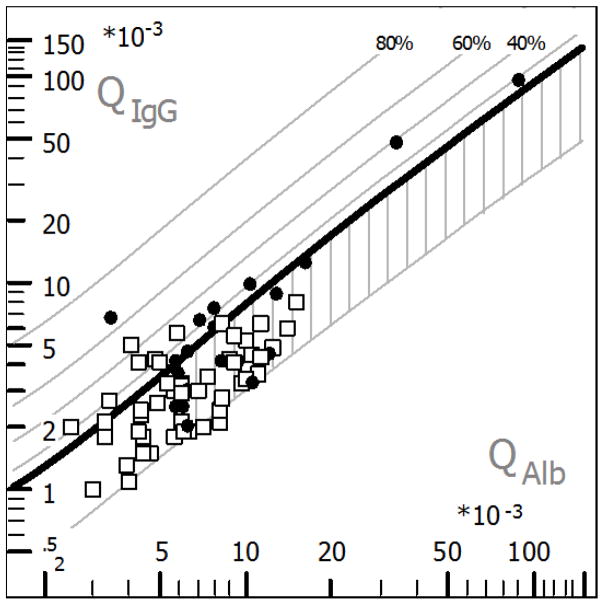
Figure 2. Hyperbolic function (Reibergram plot) of blood-CSF barrier function and intrathecal IgG synthesis in HIV positive participants.
Hyperbolic functions are a consequence of nonlinear interaction between molecular flux and CSF flow rate as derived from the laws of diffusion (Reiber, 1995). Filled circles are participants HIV+ with CSF WBC > 5 cell/mm3, while open squares are participants HIV+ with CSF WBC < 5 cell/mm3. The age-corrected normal range of QAlb was 7 × 10−3, as indicated in the graphic. BCSFB dysfunction (area with vertical stripes) was observed in 12 (60 %) participants with white blood cell count > 5 cell/mm3, as well as in 20 (41.67 %) participants with white blood cell count < 5 cell/mm3 (χ2 P = 0.192). Intrathecal IgG synthesis was present in nine cases in both groups, at a prevalence of 45 % and 18.75 % respectively (χ2 P = 0.05). BCSFB barrier dysfunction was noted in five of these participants, all of whom presented pleocytosis. The plot was generated with CSF Research software.