Figure 5.
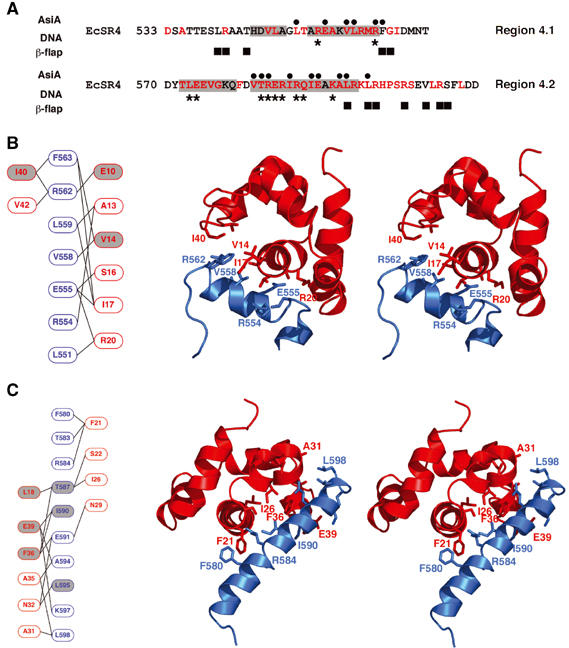
Detailed interaction between AsiA and EcSR4. (A) Comparison of AsiA-binding positions in the EcSR4 complex (black dots) versus the contact regions between SR4 and DNA (asterisks; Campbell et al, 2002) or the β-flap tip helix (black squares; Vassylyev et al, 2002). The interaction with AsiA overlaps both DNA and core RNAP-binding sites of SR4. The helices present in EcSR4 are indicated by gray shading and conserved amino acids are shown in red. (B) Subdomain I of the AsiA/EcSR4 interaction. Subdomain I is composed of helix A1 of AsiA and helix S2 of EcSR4. Schematic overview of contacting residues in the subdomain is shown in red and blue for AsiA and EcSR4, respectively, in the left panel. Gray shading indicates positions of AsiA, which are defective for EcSR4 binding in a pulldown assay (Lambert et al, 2001) or cellular toxicity experiment (Sharma et al, 2002; Pal et al, 2003). The right panel displays a stereoview of the subdomain, viewed down the axis of helix A1 in the complex, with selected side chains displayed on a ribbon representation of the backbone. The structure of the complex shown is a representative choice of one model from the structure family. (C) Subdomain II of the AsiA/EcSR4 interaction. Subdomain II is composed of the C-termini of helices A1, A3 and all of helix A2 of AsiA contacting helix S4 of EcSR4. A schematic overview of contacting residues in the subdomain is shown in red and blue for AsiA and EcSR4, respectively, in the left panel. Gray shading indicates positions of AsiA or EcSR4, which are defective for binding in a pulldown assay (Lambert et al, 2001) or cellular toxicity experiment (Sharma et al, 2002; Pal et al, 2003). The right panel displays a stereoview of the subdomain, viewed down the axis of helix A1 in the complex, with the side chains of the indicated residues in the schematic displayed on a ribbon representation of the backbone. The structure of the complex shown is an arbitrary choice of one model from the structure family. Note that the orientations of the stereo pairs in (B) and (C) differ by a 180° rotation about the horizontal axis.
