Figure 6.
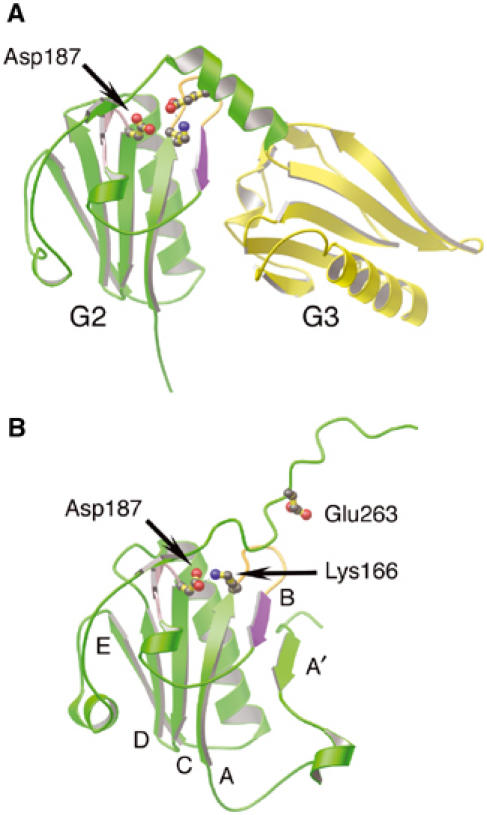
Regions of gelsolin implicated in FAF. (A) Ribbon representation of G2 (green) and G3 (yellow) excised from the G1–G3:actin complex structure (1RGI). The loop preceding the C strand (pink), the A–B loop (orange) and the B strand (purple), containing the protease-sensitive site of FAF gelsolin (Arg172–Ala173), are highlighted. Residue Lys166 is depicted forming a salt bridge to Glu263, and the locus of FAF mutation, residue Asp187, is drawn. (B) Ribbon representation of G2 (green) from inactive gelsolin (PDB 1D0N; Burtnick et al, 1997). The FAF mutation residue, Asp187, is depicted forming an ion pair with Lys166. Residue Glu263 is also drawn. The β-strands are identified by letter. Mutation of Asp187, we propose, results in trapping G2–G3 between active (A) and inactive (B) states, increasing accessibility of the critical bond in the B strand (purple).
