Figure 8.
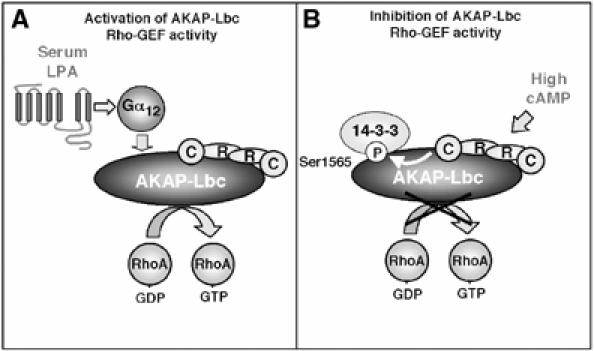
Model for the 14-3-3-mediated inhibition of AKAP-Lbc. (A) AKAP-Lbc is activated in response to serum or LPA stimulation through a Gα12-mediated signaling pathway. (B) Elevation of the cellular concentration of cAMP activates the PKA holoenzyme anchored to AKAP-Lbc. The catalytic subunit released from the PKA holoenzyme can phosphorylate AKAP-Lbc on serine 1565. This induces the recruitment of 14-3-3, which inhibits the Rho-GEF activity of AKAP-Lbc.
