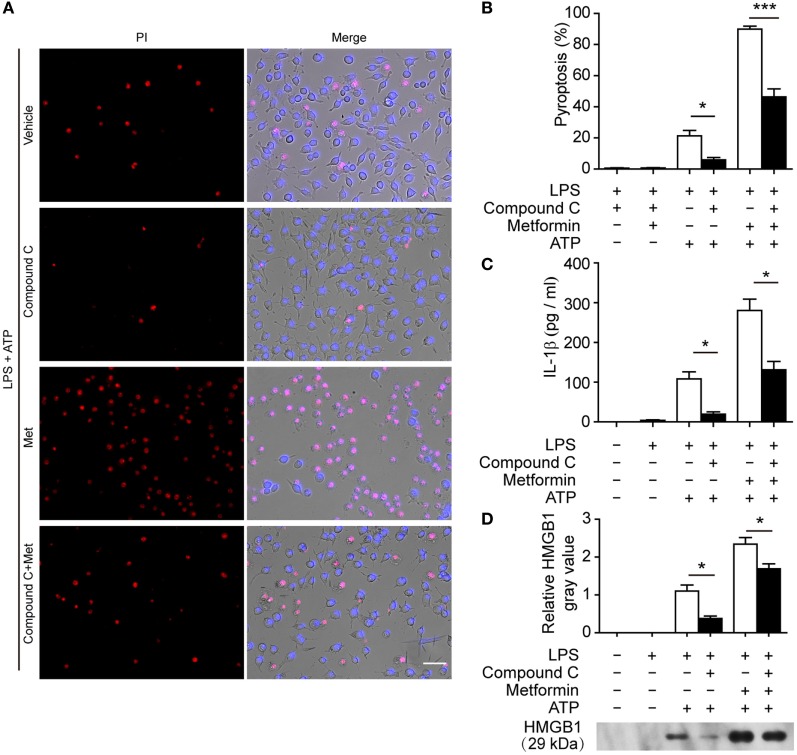
Figure 7.
Pharmacological blockade of AMP-activated protein kinase signaling suppressed adenosine triphosphate (ATP)− or ATP+ metformin-induced pyroptosis in J774A.1 cells. J774A.1 cells were first primed with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (500 ng/ml) for 4 h, and then pretreated with compound C (20 µM in Opti-MEM) for 1 h and metformin (2 mM in Opti-MEM) for 1 h. Subsequently, 3 mM ATP was added to the medium for 30 min. (A) Pyroptotic cells were revealed by their fluorescence of propidium iodide (PI) (red) staining and the nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342 (blue, for all cells). The images of PI and Hoechst 33342 staining were merged with bright-field images. Scale bar, 50 µm; Met, metformin. (B) Pyroptosis ratios were calculated by the number of PI-positive cells relative to the total number of cells in five random fields each containing about 100 cells. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 5). (C) The levels of soluble interleukin-1β in the supernatants were evaluated by cytometric bead array assay (n = 3). (D) Soluble HMGB1 in the culture supernatants were precipitated and evaluated by western blotting, setting the blot gray value of LPS + ATP group as 1.0 (n = 3). *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001.