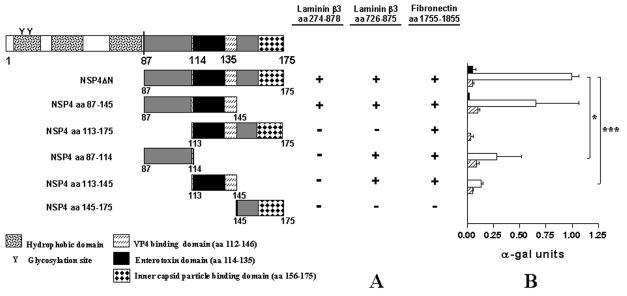
FIG. 5.
Binding domain analysis of NSP4 with laminin-β3 (aa 274 to 878), laminin-β3 (aa 726 to 875), and fibronectin (aa 1755 to 1885). (A) NSP4ΔN was fragmented into five subclones by PCR. Bars represent truncated NSP4 clones fused to the GAL4 binding domain. Amino acid positions are indicated. Yeast strain AH109 was cotransformed with the laminin-β3 clones and pGBKT7-NSP4ΔN. The interactions were assessed by checking for blue colonies in the presence of X-α-Gal. Functional and structural domains of NSP4 are presented in boxes. (B) Quantitative analysis of the interactions were obtained from independent yeast cotransformants assayed with p-nitrophenyl-α-d-galactosidase as a substrate. α-Galactosidase activity was expressed in units and calculated by the following formula: (OD410 × Vf × 1,000)/[OD600 × T × (ɛ × b) × Vi], where OD410 is the absorbance of the reaction mixture measured by optical density at 410 nm, OD600 is the optical cell density of the culture at 600 nm, T is the reaction time in minutes, Vf is the total volume (in milliliters) of the assay, Vi is the volume of culture medium supernatant added, ɛ is the molar absorbtivity for p-nitrophenol, and b is the light path in centimeters. Solid, open, and striped bars correspond to interactions of laminin-β3 (D19 clone), laminin-β3 (aa 726 to 875), and fibronectin (clone D22) with the NSP4 constructs, respectively, indicated. Standard errors of the mean are shown for the results of three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001 by Student's t test.