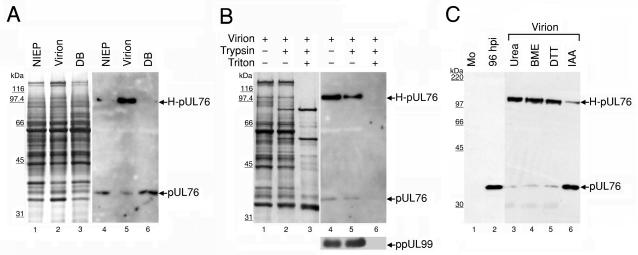
FIG. 3.
Association of pUL76 with gradient-purified HCMV particles. (A) Protein composition of three distinct viral particles. The released viral particles were purified, and equal amounts of the viral proteins were resolved on an SDS-10% polyacrylamide gel and visualized by silver staining (lanes 1 to 3). The presence of pUL76 within viral particles was analyzed by Western blotting with an anti-pUL76 antibody (lanes 4 to 6). Lanes 1 and 4, noninfectious enveloped particles (NIEP); lanes 2 and 5, virions; lanes 3 and 6, dense bodies (DB). (B) Demonstration that pUL76 is associated with HCMV virions and is insensitive to trypsin digestion. Purified virions were treated with trypsin in the presence (+) or absence (−) of Triton X-100. The proteins were resolved after digestion on an SDS-10% polyacrylamide gel. The presence of proteins was analyzed by Western blotting with an anti-pUL76 antibody and, as a control, with an anti-ppUL99 antibody. (C) Evidence that H-pUL76 within the virions is derived from pUL76. Lanes: 1, Western blot of lysate prepared from mock-infected (Mo) HEL cells; 2, cell lysate at 96 h postinfection; 3 to 6, gradient-purified virions treated with 6 M urea (lane 3), 10% β-mercaptoethanol (BME; lane 4), 200 mM dithiothreitol (DTT, lane 5), or 135 mM iodoacetamide (IAA, lane 6). The sizes of molecular mass markers are indicated on the left.