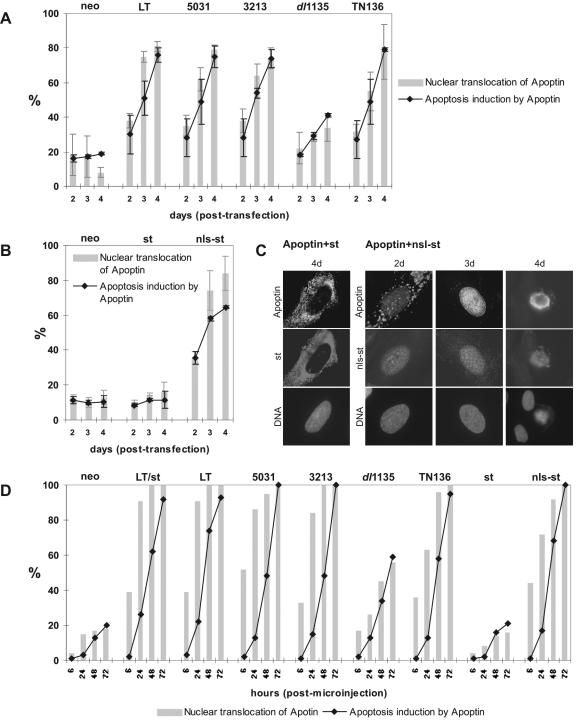
FIG. 4.
Apoptin is activated by an N-terminal determinant of LT. (A) Differential activation of apoptin by a collection of SV40 LT mutants. pCMV-VP3 was cotransfected in VH10 cells with pRSV-LT (wild-type LT), pRSV-3213 (pRb binding mutant), pRSV-5031 (p53 binding mutant), dl1135 (J domain deletion), and pRSV-TN136 (truncated LT containing N-terminal 136 aa), and pCMV-neo as a negative control. Three separate cotransfection experiments were performed. Cells were analyzed 2, 3, and 4 days posttransfection. Immunofluorescence analysis was performed as described in the text, except that the expression of dl1135 was determined by antibody KT3. (B) Activation of apoptin by the NLS-tagged SV40 st (nls-st). Cotransfection experiments were carried out with VH10 cells with pCMV-VP3 and pRSV-st encoding st, pRSV-nls-st expressing nls-st, and pCMV-neo as a control. Two separate experiments were performed. (C) Immunofluorescence images showing apoptin inactive in the presence of cytoplasmic st (first panel) but active in nuclear translocation (second and third panel) and cell killing (fourth panel) triggered by nuclear nls-st. (D) Reproducibility of the effect of SV40 proteins (wild type and mutant) on the activation of apoptin, confirmed by using an alternative DNA transduction strategy, microinjection. Comicroinjected VH10 cells were analyzed 6, 24, 48, and 72 h postmicroinjection.