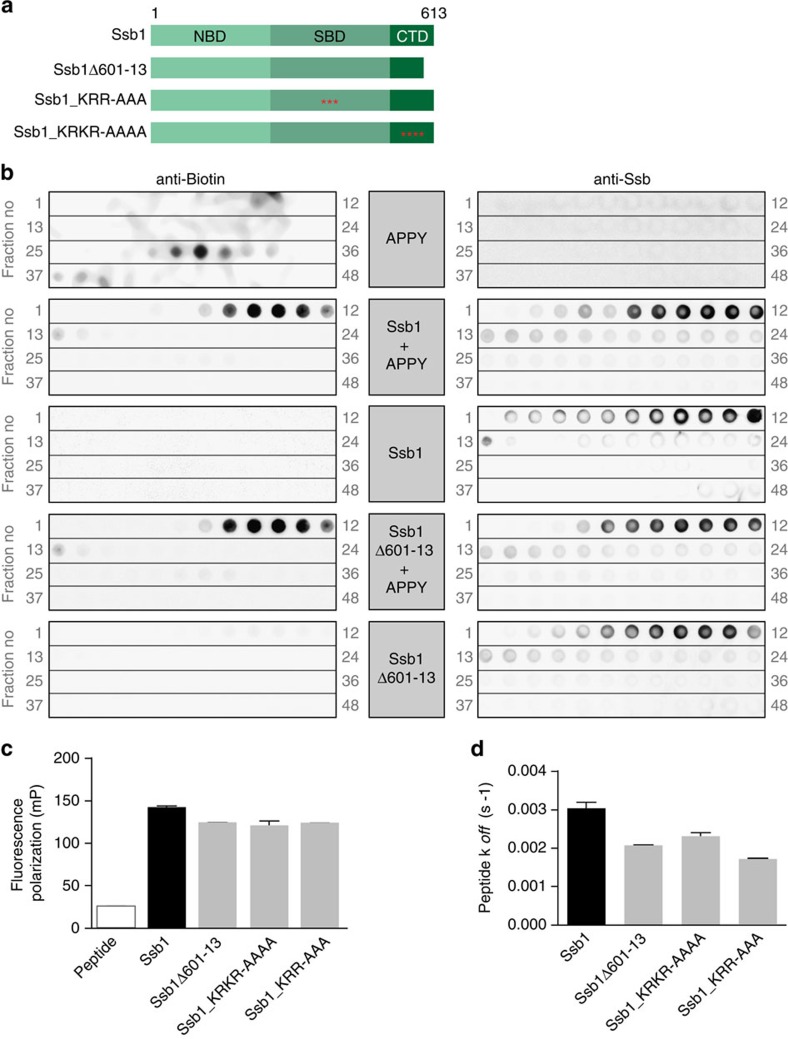
Figure 5. Wild type and mutant Ssb1 interact with canonic Hsp70 substrate peptides in vitro.
(a) Schematic overview of Ssb domains and the constructs used. Ssb1Δ601–13 lacks 13 C-terminal residues; red asterisks mark point mutations (Ssb1_KRR428AAA; Ssb1_KR603AA-K608A-R613A). (b) Analysis of wild type (wt) and mutant Ssb1 interaction with APPY-peptide analysed via gel filtration. Biotin labelled APPY peptide was incubated alone or with either wt or mutant Ssb1. Ssb1 or Ssb1Δ601-13 alone served as controls. Samples were applied to size exclusion chromatography to separate free peptide from Ssb-bound one. The resulting elutions were fractionated and spotted from high to low molecular weight (grey numbers indicate fractions) onto nitrocellulose membranes followed by immunological detection of either APPY (via HRP-StrepTactin) (left) or Ssb1 (right). (c) Peptide binding analyses of wt and mutant Ssb1 using fluorescence anisotropy. Wt or mutant Ssb1 was incubated with (IAANS)-labelled peptide σ32-Q132-Q144-C followed by fluorescence polarization measurements. (d) Peptide release kinetics of wt or mutant Ssb1 using (IAANS)-labelled peptide σ32-Q132-Q144-C. Error bars represent s.e.m. of at least three independent experiments.