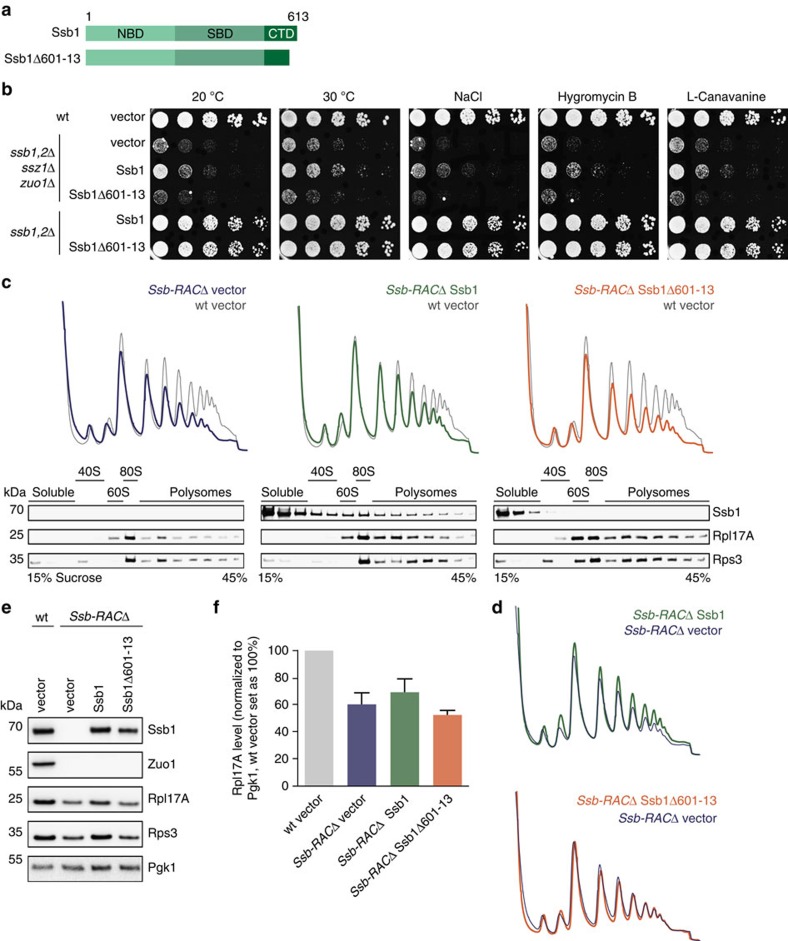
Figure 6. The Ssb1Δ601-13 ribosome-binding mutant needs its co-factor RAC for in vivo functionality.
(a) Schematic overview of Ssb domains and the constructs used. Ssb1Δ601–13 lacks 13 C-terminal residues. (b) Growth analysis of wild type (wt), ssb1,2Δssz1Δzuo1Δ (Ssb-RACΔ) and ssb1,2Δ cells transformed with empty vector or Ssb1 constructs. Exponentially growing cells were adjusted to OD600=0.4 and spotted in fivefold serial dilutions onto SC-URA plates (that may contain certain additives), which were incubated at 30 °C for two days or at 20 °C for five days. (c) For polysome profiling wt cells transformed with empty vector (grey) or Ssb-RACΔ cells transformed with either empty vector (blue) or different Ssb1 constructs (green, orange) were grown in SC-URA media to early exponential phase. Lysates were adjusted and 18 A260 units on top of a linear 15–45% (w/v) sucrose gradient were ultracentrifuged followed by gradient fractionation from top to bottom and OD254 monitoring (top). Fractions were analysed via immunoblotting (bottom). The wt profile (grey) at the background of each profile served as control. (d) Overlay of polysome profiles of Ssb-RACΔ cells transformed with Ssb1 (green) or Ssb1Δ601–13 (orange) with the empty vector control (blue) as shown in c. (e) Protein expression analysis of wt cells transformed with empty vector or Ssb-RACΔ cells transformed with either empty vector or different Ssb1 constructs. Cells were grown to early exponential growth phase in SC–URA media, harvested and lysed. Lysates were adjusted to the same protein concentration and analysed via SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting. (f) Quantification of Rpl17A protein levels as shown exemplarily in e. Rpl17A signals were normalized to Pgk1 loading control and wt cells transformed with empty vector were set as 100%. Error bars represent s.e.m. of at least three independent experiments.