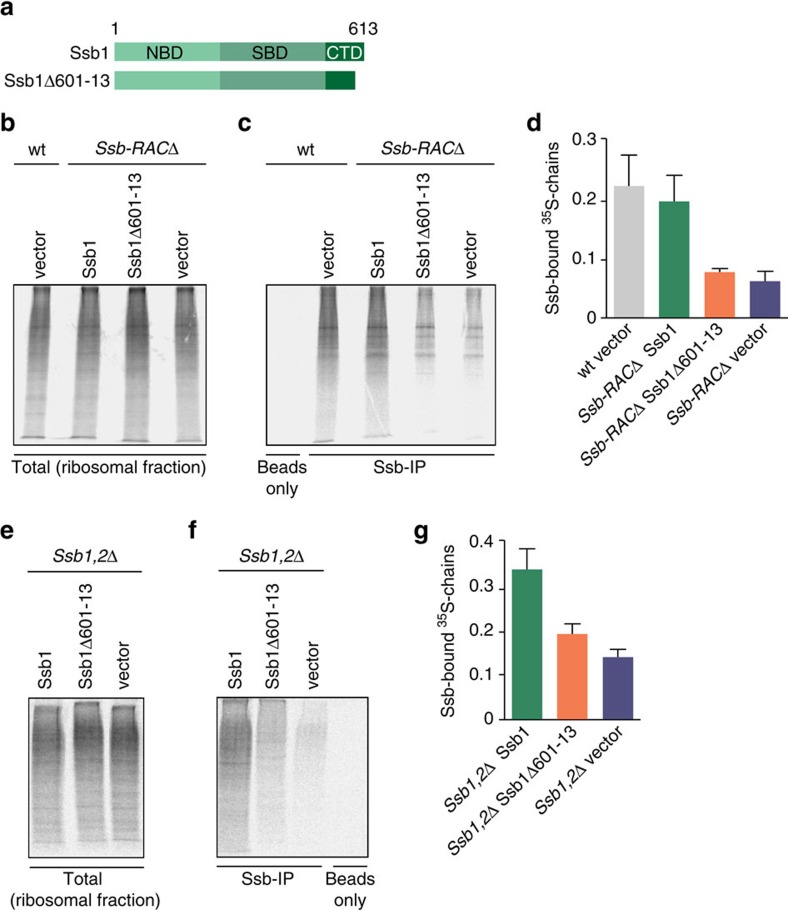
Figure 7. A ribosome-binding mutant of Ssb critically depends on RAC for efficient nascent chain interaction.
(a) Schematic overview of Ssb domains and the constructs used. Ssb1Δ601–13 lacks 13 C-terminal residues. Wild type (wt), ssb1,2Δ or ssb1,2Δssz1Δzuo1Δ (Ssb-RACΔ) cells were transformed with either empty vector, wt Ssb1 or Ssb1Δ601–13. Cells were grown to OD600=0.5, starved for 30 min in -Met medium and pulsed with 35S-Met for 1.5 min. Cells were harvested, lysed and ribosomal pellets were isolated using a 25% (w/v) sucrose cushion. Ssb immunoprecipitations (IPs) were performed using Ssb antibody crosslinked to ProteinG dynabeads. (b) Autoradiogram of 35S-labelled nascent chains from ribosomal pellets of transformed wt or Ssb-RACΔ cells. (c) Immunoprecipitation of Ssb-associated RNCs (ribosome nascent-chain complexes) from ribosomal pellets of transformed wt or Ssb-RACΔ cells. (d) Quantification of Ssb-associated RNCs from ribosomal pellets of the different strains as shown in c compared with corresponding ribosomal pellets as shown in b. (e) Autoradiogram of 35S-labelled nascent chains from ribosomal pellets of transformed Ssb1,2Δ cells. (f) Immunoprecipitation of Ssb-associated RNCs from ribosomal pellets of transformed Ssb1,2Δ cells. (g) Quantification of Ssb-associated RNCs from ribosomal pellets of the different strains as shown in f compared with corresponding ribosomal pellets as shown in e. Error bars represent s.e.m. of at least three independent experiments.