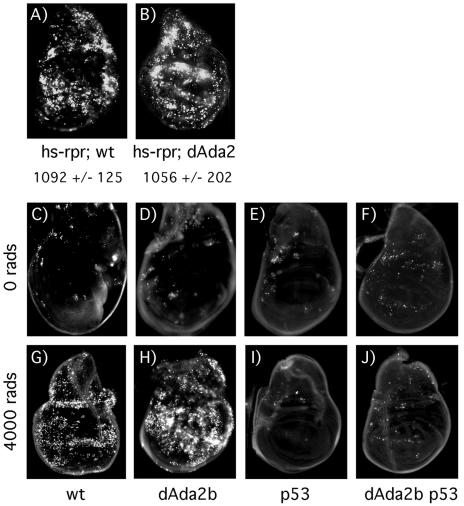
FIG. 6.
dAda2b acts upstream of reaper in p53-dependent apoptosis. (A and B) Wild-type (wt) and dAda2b mutant third-instar larvae containing an hs-reaper transgene (hs-rpr) were heat shocked, and wing imaginal disks were incubated in acridine orange after a 1-h recovery period. Similar numbers of apoptotic cells are observed in wt (A) (1,092 ± 125 stained cells) and dAda2b mutant (B) (1,056 ± 202 stained cells) wing disks containing the hs-reaper transgene. (C to J) Radiation-induced apoptosis in dAda2b mutants is p53 dependent. wt (C and G), dAda2b mutant (D and H), p53 mutant (E and I), and dAda2b p53 double mutant (F and J) third-instar larvae were mock treated or irradiated with 4,000 rads. After 4 h, wing imaginal disks were dissected and incubated in acridine orange. Very few apoptotic cells are observed in mock-treated wt (C), dAda2b mutant (D), and p53 mutant (E) wing disks. Slightly more apoptotic cells are found in mock-treated dAda2b p53 double mutant wing disks (F). In response to 4,000 rads of irradiation, massive apoptosis is observed in wt wing disks (G), and even more is observed in dAda2b mutant wing disks (H). As expected, no apoptosis is found in p53 mutant wing disks (I). In dAda2b p53 double mutant wing disks (J), there is no increase in the amount of apoptosis compared to mock-treated disks (F).