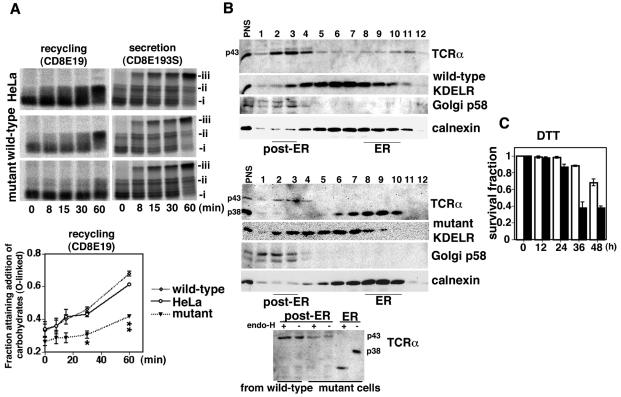
FIG. 1.
Transport mutant KDEL receptor perturbed recycling of misfolded proteins between the ER and the Golgi complex. (A) Cells were transiently transfected with CD8E19 or CD8E193S. Addition of ER-specific N-linked glycosylation (i), cis-Golgi-specific O-linked glycosylation (ii), or Golgi-specific N-linked glycosylation (iii) was assessed by pulse-chase experiments followed by immunoprecipitation with an anti-CD8 monoclonal antibody. The recycling of CD8E19 was assessed by calculating the fraction with O-linked glycosylation (ii/[i + ii]) by densitometry. The line graph represents the mean value ± standard error from three experiments. Statistical analyses were performed with analysis of variance and the Scheffe test among the three groups. The values in the mutant cells at 30 min (*, 0.306 ± 0.023) and 60 min (**, 0.417 ± 0.012) were significantly different from those in HeLa cells (0.429 ± 0.014 and 0.612 ± 0.010, respectively) and wild-type cells (0.459 ± 0.015 and 0.678 ± 0.015, respectively). *, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.0001. (B) The distribution of TCRα, KDEL receptors, Golgi p58, and calnexin in wild-type (upper panel) and mutant KDEL receptor (middle panel) stable cells on a continuous sucrose gradient (top, fraction 1; bottom, fraction 12) was determined by Western blotting. Aliquots of the ER (fraction 9 in the middle panel) and the post-ER (fraction 3 in both the upper and middle panels) fractions were digested with endoglycosidase H and analyzed by SDS-PAGE, followed by Western blotting with a rabbit anti-murine TCRα antiserum (lower panel). (C) Wild-type (white columns) and mutant KDEL receptor (black columns) stable cells were treated with dithiothreitol (5 mM) for 0 to 48 h. After collection of the cells, cell viability was determined by trypan blue staining. The graph represents the mean value ± standard deviation of the surviving fraction from three experiments.