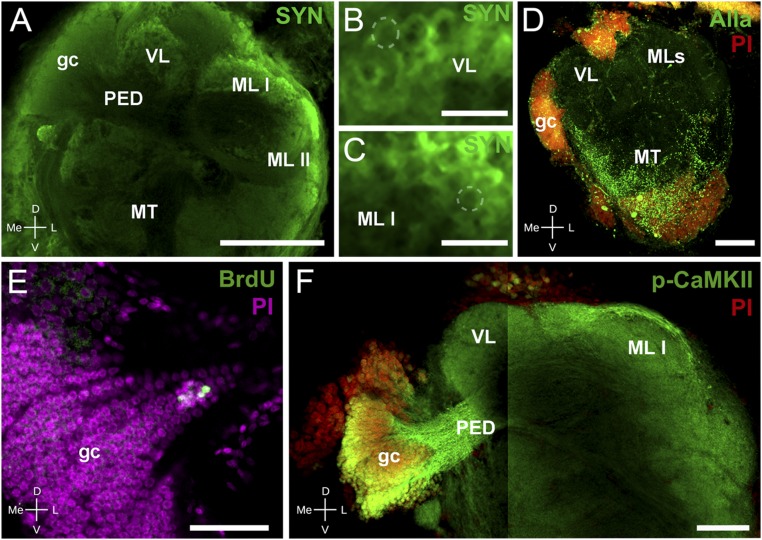
Fig. 2.
Immunohistochemistry and neurogenesis in Neohelice’s HBs. (A–C) Confocal laser scan of the lateral protocerebrum labeled with antibodies against SYN (green). (A) The gc somata cluster, the pedunculus, and both the vertical and medial lobes (medial lobes I and II) composing the HB can be distinguished. (B) Detail of the vertical lobe showing traits resembling microglomeruli (dashed line points out an example). (C) Same as B for the medial lobe I. (D) Maximum projection of confocal laser scan sections showing immunoreactivity against allatostatin (Alla, green) and nuclei stained with propidium iodide (PI, red). Alla-like immunoreactivity appears widely distributed in the medulla terminalis, whereas there is scarce immunoreaction in the area corresponding to the HB. (E) Confocal laser scan sections of the HB-gc somata labeled with antibody against BrdU (green) and with PI (magenta) visualizing newborn cells in the gc cluster. (F) Confocal laser scan of the HB labeled with antibodies against p-CAMKII-α (green) and with PI (red). The image is composed of two stacks taken at different focal planes. (Left) The gc, comarked p-CAMKII-α and PI, and the pedunculus that projects toward the vertical and medial lobes. (Right) Pedunculus projecting toward both medial lobes. Abbreviations are as in Fig. 1. (Scale bars: A, 200 μm; B and C, 20 μm; D and F, 100 μm; E, 50 μm.)