FIG. 7.
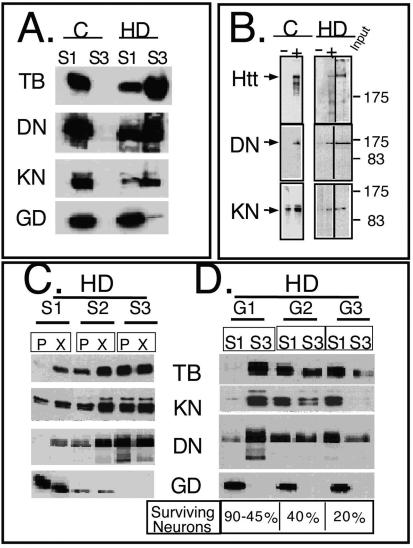
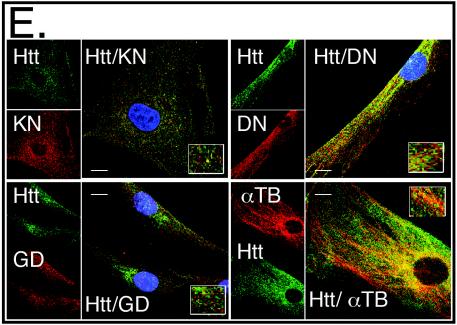
mhtt causes redistribution of soluble htt, cytoskeletal proteins, and trafficking motors to poorly soluble S3 extracts of human HD-affected brain. (A) An equal amount of total protein was analyzed for solubility by comparing S1 and S3 extracts by immunoblotting. Trafficking proteins α-tubulin (TB), dynactin (DN), and kinesin (KN) are present only in the S1 extract of control brain but are redistributed to the S3 extract in the HD-affected human brain. Control (C) and HD-affected brain extracts are from the caudate and putamen regions. GAPDH (GD) remains in the S1 of both control and HD-affected brain. (B) Trafficking proteins interact with both normal and mhtt in human brain. Immunoprecipitation of htt, dynactin, and kinesin from an S1 extract of control brain or from S3 gel filtration fractions of HD-affected brain. Since no htt was present in the S3 extract of control brain, it was not analyzed. Immunoprecipitation utilized the 2166 htt antibody; −, protein G beads alone; +, protein G beads cross-linked with antibody. Input is 8% of the protein sample in the immunoprecipitation reactions. (C) Reduced solubility of α-tubulin, kinesin, and dynactin in the brain regions vulnerable to HD. An equal amount of total protein from the S1, S2, and S3 extracts of grade 1 caudate-putamen (P) or cerebral cortex (X) was analyzed by immunoblotting. The motor-associated proteins are enriched in the poorly soluble S3 extract. The control protein GAPDH is found predominantly in the soluble S1 extract. (D) Solubility of trafficking proteins as a function of disease severity. An equal amount of total protein from S1 and S3 extracts from the caudate and putamen of three HD-affected brains of grade 1 (G1), 2 (G2), and 3 (G3) were probed for α-tubulin, kinesin, dynactin, and GAPDH. The level of α-tubulin, kinesin, and dynactin in S1 increases with grade and decreases with the average number of surviving neurons characteristic of each grade as previously described (44). The level of proteins in S3 shows the inverse pattern. The control protein GAPDH remains totally soluble in both control and HD-affected brains. (E) Colocalization of htt and trafficking proteins in fibroblasts from control individuals and HD patients. Note colocalization of htt with kinesin, α-tubulin, and dynactin but not with GAPDH. In all panels, htt is green; kinesin, dynactin, GAPDH, and α-tubulin are red; blue indicates the nucleus. Overlays are indicated. Confocal images were taken with 100× oil DIC (1.4 n.a.), thickness of the slices was ∼0.5 μm. Scale bar, 10 μm.