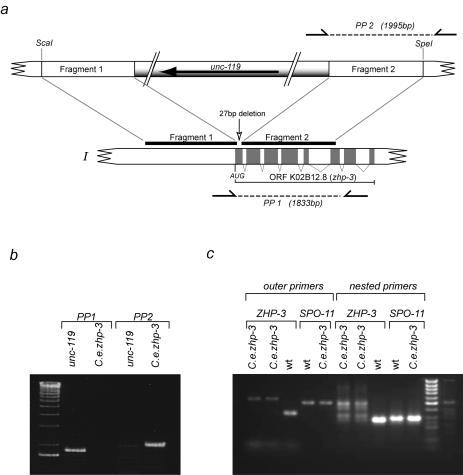
FIG. 1.
(a) Map of the K02B12.8 locus on chromosome I. Fragment 1, encompassing the promoter and part of the first exon, and fragment 2, stretching from exon 1 to exon 7, were cloned into plasmid PD#MM016 containing the unc-119 rescuing locus. After cleavage with ScaI and SpeI, the disruption cassette was used for homologous integration. PP1 and PP2 denote the primer pairs used for diagnostic PCR. (b) Diagnostic PCR. PP2 primes in the unc-119 sequence in the targeting cassette and in the K02B12.8 locus outside the fragment that was cloned into the targeting cassette and amplifies a fragment of about 1.9 kb in the case of homologous integration but not in untransformed worms. PP1 primes in the K02B12.8 locus and amplifies a product of 1.8 kb from the undisrupted locus. In the case of the homologously tagged mutant, the PCR conditions applied did not allow the amplification of the expected 7-kb product. (c) Reverse transcription-PCR on the mutant (jf-61) to prove the absence of the K02B12.8 transcript. PCR on cDNA of jf-61 did not result in a detectable band of the expected size (lanes 1 and 2); even a nested PCR of those samples did not amplify a transcript (lanes 6 and 7). Lanes 3 and 8 prove that the zhp-3 primer pairs do amplify the expected bands of 341 and 276 bp from wild-type cDNA. Primer pairs from a spo-11 cDNA do amplify bands of the expected sizes (501 and 296 bp) from both the wild type cDNA pool (lanes 4 and 9) and the mutant cDNA pool (lanes 5 and 10).