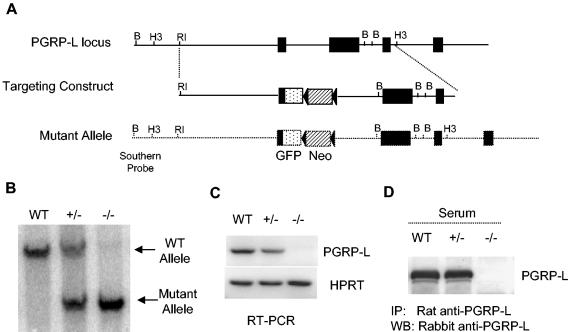
FIG. 2.
Generation of PGRP-L-deficient mouse. (A) The PGRP-L gene locus is depicted as a single line, with exons represented as filled boxes. Relevant restriction enzyme sites are shown. B, BamHI; H3, HindIII; RI, EcoRI. The organization of the targeting construct and the arrangement of the recombined PGRP-L allele are also shown. The dotted box indicates the GFP cassette that was engineered in-frame with the PGRP-L ATG start codon. The drug selection neomycin cassette (Neo) is depicted as a striped box, with two flanking loxP sites depicted as filled triangles. (B) Genotyping with Southern blot analysis. Tail DNA was subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis. The presence of the mutant allele (7.5 kb) and the wild-type allele (9.6 kb) was determined by Southern blotting, using a probe upstream of the homologous recombined sequence. (C) RT-PCR assay to determine PGRP-L expression. Liver RNA from wild-type, heterozygous, and homozygous gene-targeted mice was extracted and reverse transcribed into cDNA. PGRP-L expression was determined by PCR. The expression of hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase was used as a control. (D) Serum from wild-type, heterozygous, and homozygous gene-targeted mice was immunoprecipitated using rat anti-PGRP-L antibodies. The immunoprecipitates were blotted with rabbit anti-PGRP-L antibodies.