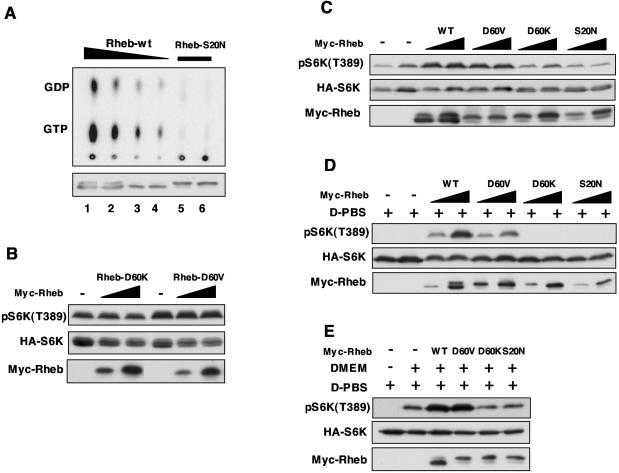
FIG. 3.
Characterizations of potential dominant-negative Rheb mutants. (A) Rheb-S20N is defective in nucleotide binding. Wild-type Rheb (Rheb-wt) and Rheb-S20N were transfected into HEK293 cells. The transfected cells were labeled with [32P]phosphate. The bound nucleotides (top) of immunoprecipitated Rheb (bottom) are shown. (B) Rheb-D60V and Rheb-D60K do not inhibit S6K phosphorylation. HA-S6K was cotransfected with Rheb mutants in HEK293 cells. Thirty minutes before harvesting, cells were stimulated with fresh DMEM with 10% fetal bovine serum. Phosphorylation of S6K was determined by Western blotting. (C) Rheb-D60V, RhebD60K, and Rheb-S20N do not function as dominant negatives. Experiments are similar to those described above (B), except that cells were not stimulated by fresh medium. (D) Rheb-D60V activates S6K. The transfected HEK293 cells were treated with D-PBS (PBS containing 45 mM glucose) for 30 min before harvesting. (E) Rheb-D60V and Rheb-D60K do not block S6K activation by DMEM. The transfected HEK293 cells were treated with D-PBS for 30 min followed by treatment with DMEM (as indicated) without serum for 30 min before harvesting. WT, wild type.