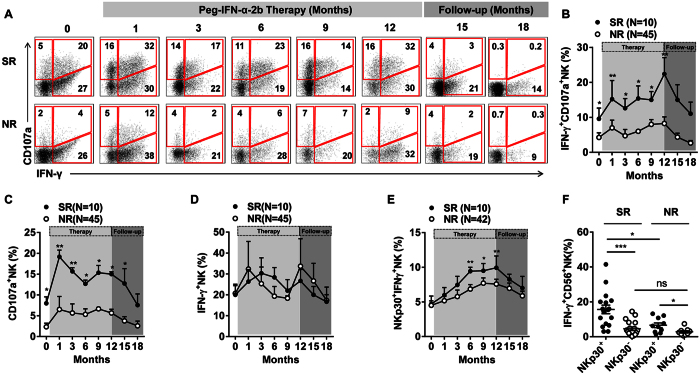
Figure 4. Peg-IFN-α-2b regulated NK cell function by increasing degranulation and IFN-γ expression, which correlated with clinical outcomes.
(A) Longitudinal analysis of IFN-γ and CD107a co-expression by NK cells in the SR and NR patients. (B–D) The frequencies of IFN-γ+ CD107a+ NK, CD107a+ NK, and IFN-γ+ NK cells during Peg-IFN-α therapy and follow-up. (E) Longitudinal analysis of IFN-γ expression by NKp30+ NK cells in the SR and NR patients. (F) IFN-γ expression by NKp30+ NK cells in the SR and NR patients at the end of Peg-IFN-α therapy. Horizontal bars indicate the mean values with the standard error of the mean. Analyses of unpaired data were performed using the Mann-Whitney U-test, and analyses of paired data were performed using the Wilcoxon test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.