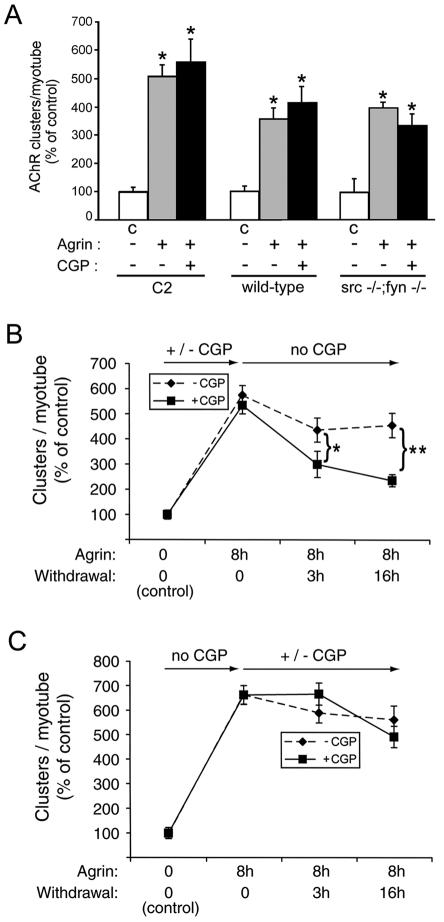
FIG. 5.
SFK activity during cluster formation is required for cluster stabilization later on. (A) Myotubes were stimulated overnight with 0.5 nM agrin in the presence or absence of CGP77675 (CPG), stained with rhodamine-α-BT, and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. AChR clustering was quantitated and is shown as the percentage of untreated cells (C, control) (means ± SEM of at least three experiments). An asterisk indicates that the result differs significantly from that for the respective untreated cells (P < 0.03) but not from each other (P > 0.09; two-tailed paired t test), showing that CGP77675 does not inhibit agrin-induced formation of AChR clusters. (B) C2 myotubes were treated with 0.5 nM agrin for 8 h in the presence (squares) or absence (diamonds) of CGP77675, followed by withdrawal (for 3 or 16 h) of both CGP77675 and agrin, as indicated by arrows. AChR clustering was quantitated as described for panel A, showing no difference in the number of clusters formed, but the clusters dispersed more rapidly in CGP77675-treated cells (*, P < 0.03; **, P < 0.001; two-tailed paired t test). (C) C2 myotubes were stimulated for 8 h with agrin, followed by withdrawal of agrin and addition (squares) or no addition (diamonds) of CGP77675 into the agrin-free medium. After 3 or 16 h of withdrawal, AChR clustering was quantified as described for panel A, revealing no differences between CGP77675-treated and untreated cells (P > 0.2).