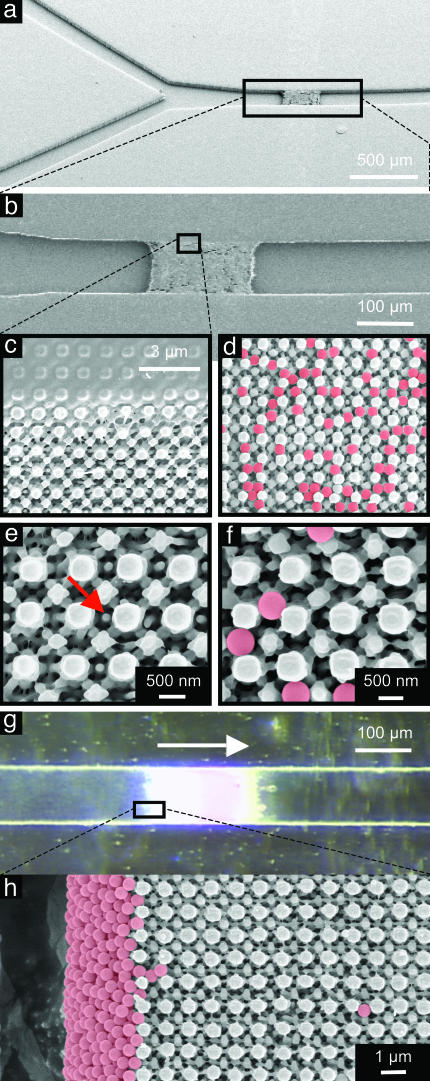
Fig. 5.
SEMs and optical micrographs of a 3D nanostructure built into the channel of a microfluidic system. The mask consists of a square array of relief features with diameters of 740 nm (rounded square), a relief depth of 420 nm, and a duty cycle of 43%. (a)A45° tilted view of Y-junction channel (channel width of 100 μm). (b) Magnified SEM view of 3D structure integrated into a fluidic channel. (c) Magnified view of the region near the edge of the channel. (d) Five-hundred-nanometer particles (F8812, FluoSpheres, Molecular Probes) filtered through a 3D structure. The beads are colorized for ease of viewing. (e) Magnified view of top surface structure. The red arrow indicates an ≈100-nm nanostructure. (f) Magnified view of d. (g) Flowing an aqueous suspension of 0.02% beads into the channel at the rate of 3 μl/min (arrow indicates flow direction) results in a filtering of the beads. (They remain on the left side of the filter.) (h) Filtered beads at the side wall because of the flow direction.