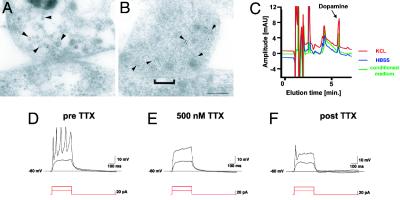
Fig. 4.
Ultrastructural and functional characterization of hES-derived DA neurons. (A and B) Electron micrographs of TH ImmunoGold-labeling (5 nm) at synaptic contacts formed between neurons derived from hES cells. Gold particles are associated with small vesicles presumably containing neurotransmitters located at the presynaptic terminal (arrowheads). (A and B) Two examples of synapses are shown: A shows recently formed immature contact with a faint membrane density and few synaptic vesicles, and B shows a more differentiated synaptic contact with a distinct postsynaptic density (bracket) and a larger number of vesicles clustered in the proximity of the cell membrane. (Scale bar, 125 nm.) (C) Representative HPLC chromatogram showing high levels of DA in the medium of rosette-derived neurons (green line: medium conditioned for 24 h, 751 ± 239 pg/ml). Relatively low levels of basal DA release were detected (blue line: exposure to buffer for 15 min, 147 ± 78 pg/ml) in contrast to very high levels of DA after 15 min of KCL-evoked depolarization (red line: 1,283 ± 421 pg/ml). Data were derived from three independent experiments. Rosette-derived neurons were patched in the whole-cell configuration in current clamp mode. (D) Action potentials were evoked by depolarizing currents at a threshold of –40 mV. (E and F) Action potentials were tetrodotoxin (TTX)-sensitive.