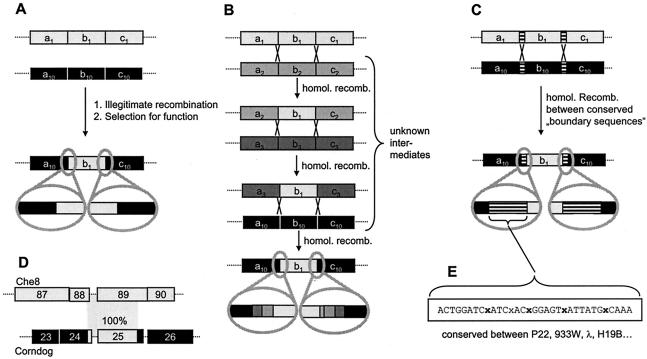
FIG. 8.
Molecular models for module exchange between phages. (A) Module exchange by illegitimate recombination. (B) Module exchange by repeated homologous recombination. This results in blocks of lower sequence identity at the border between modules. The more recombinations occur, the less easily these blocks can be recognized. (C) Module exchange by recombination via conserved linker sequences. (D) Identical (100% identity) sequence elements in different regions of two unrelated phages (177). (E) Example of a conserved linker sequence in a lambdoid phage.