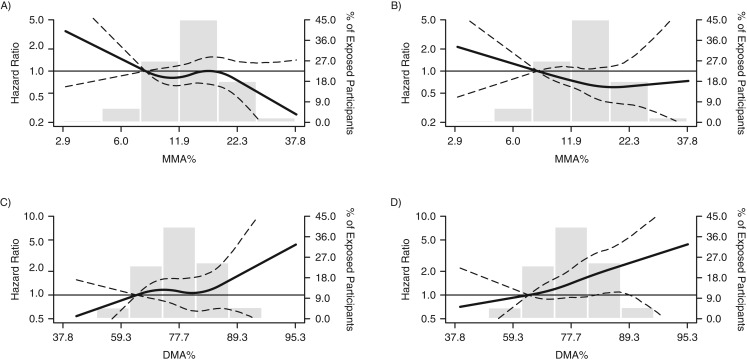
Figure 2.
Hazard ratios (HRs) for incident peripheral arterial disease (PAD) according to ankle brachial index (ABI), by arsenic metabolite level, in the Strong Heart Study, 1989–1999. The curves represent adjusted HRs for incident PAD defined as ABI <0.9 (panels A and C) or ABI >1.4 (panels B and D) based on restricted quadratic splines with knots at the 10th, 50th, and 90th percentiles of the arsenic species distribution, corresponding to 8.1%, 13.8%, and 21.4%, respectively, for percent monomethylarsonous acid (MMA%) and 65.8%, 77.9%, and 86.6%, respectively, for percent dimethylarsinous acid (DMA%). The reference value (HR = 1) was set at the 10th percentile of the arsenic species distribution (8.1% for MMA% and 65.8% for DMA%). The models adjusted for sex, age, education, smoking, body mass index, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, diabetes, hypertension, estimated glomerular filtration rate, study center, and the sum of inorganic arsenic species. The histograms (gray columns) represent the frequency distribution of urinary arsenic concentrations in the Strong Heart Study sample for 1989–1999. Dashed lines, 95% confidence intervals.