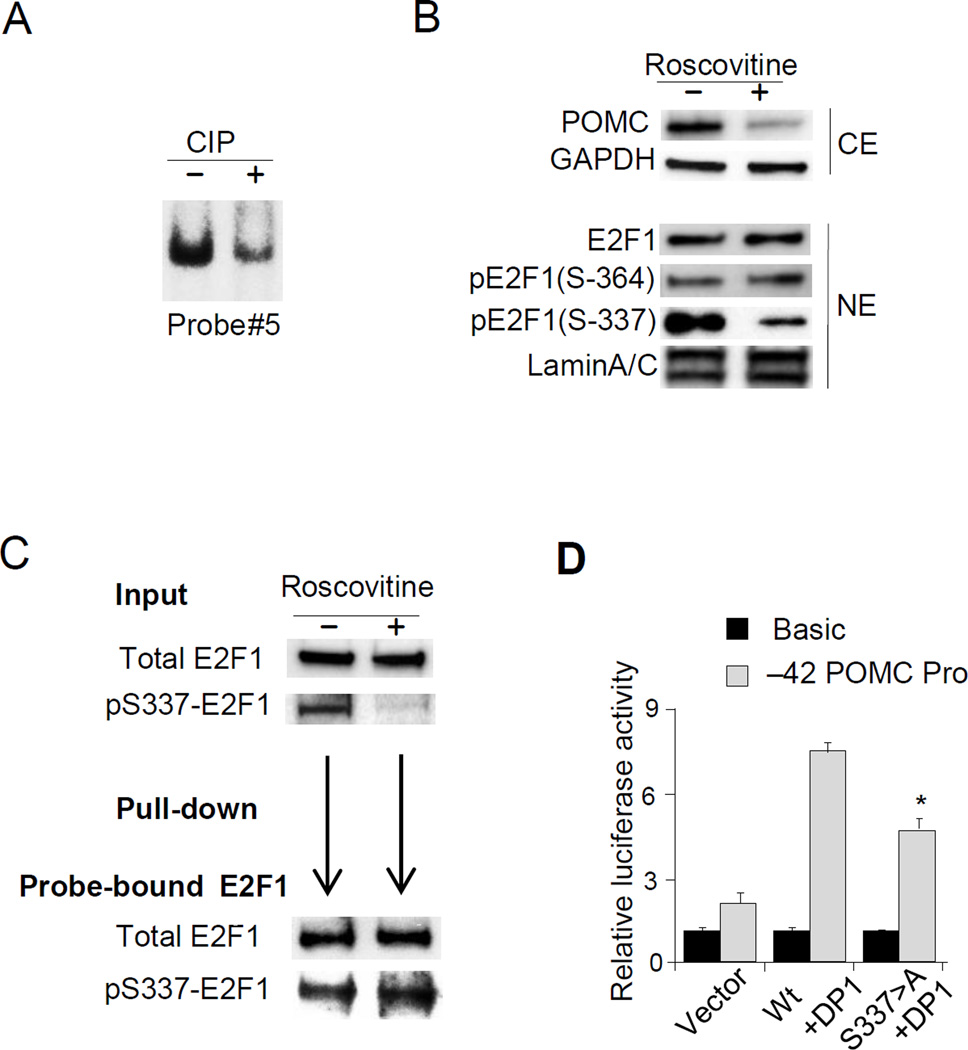
Figure 6. E2F1 Phosphorylation is required for E2F1 binding to the hPOMC promoter.
(A) Results of EMSA performed using probe #5 and nuclear extracts treated with CIP (+) or control nuclear extracts (−) incubated with CIP and CIP inhibitor (see Methods). The E2F1 complex band is shown. (B) Immunoblotting using indicated antibodies (anti-POMC, anti-GAPDH, anti-E2F1, anti-pE2F1-Ser364, anti-pE2F1-Ser337, and anti-Lamin A/C) performed using whole cell (CE) or nuclear (NE) extracts derived from DMS79 cells treated with (+) or without (−) R-roscovitine (50µM). (C) Results of immunoblotting using anti-total E2F1 and anti-pSer337-E2F1 performed with nuclear extracts (input) derived from DMS79 cells treated with (+) or without (−) R-roscovitine (50 µM). Nuclear extracts from R-roscovitine treated cells were used for DNA pull-down assay, and proteins precipitated with biotinylated probe containing E2F1 binding sites (−24/+50) (shown in Fig. 2B) were analyzed by anti-total E2F1 and anti-pSer337-E2F1. (D) Results of luciferase assays performed in COLO320 cells using the −42 hPOMC promoter (−42/+68) reporter plasmid or negative control. Wild type E2F1 or S337>A E2F1 and DP1 expression plasmids were co-transfected, and total DNA abundance adjusted with empty vector. EMSA, immunoblotting, pull-down assay, and luciferase assay results are representative of three independent experiments (A-D).