Figure 6.
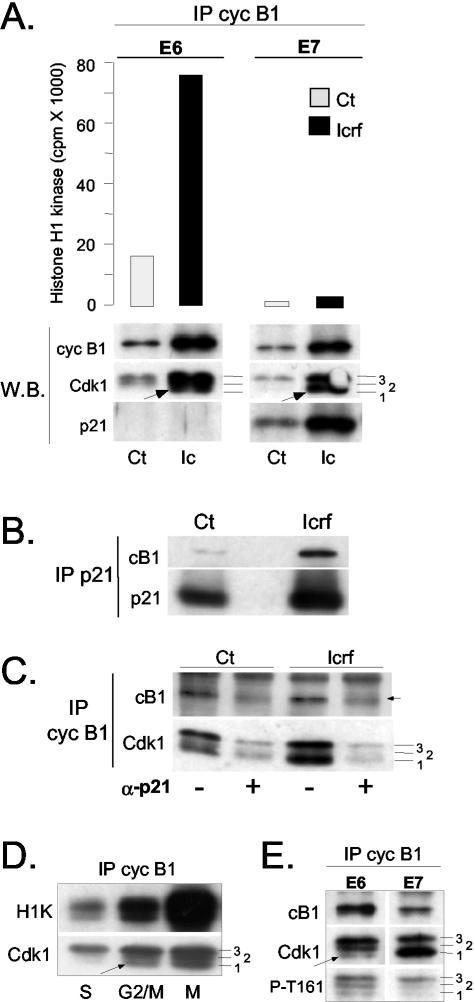
p21 binds to inactive cyclin B1-Cdk1 complexes. (A) Histone H1 kinase assays and Western blot analysis of cyclin B1 immunoprecipitates isolated from asynchronously growing control (Ct) and ICRF-193-treated E6- and E7-expressing NHFs. The same immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blot (W.B.) for the presence of cyclin B1, Cdk1 and p21. Numbers denote hyperphosphorylated (3), partially phosphorylated (2), and hypophosphorylated (1) Cdk1 isoforms (see text for more explanation). Arrows point at hypophosphorylated Cdk1 (isoform 1) that specifically accumulates in ICRF-treated cells. Note the difference in the abundance of this isoform between E6 and E7 cells. (B and C) p21 immunodepletion experiments. The protein extracts prepared from untreated (Ct) and ICRF-193-treated cells were immunodepleted for p21-bound complexes as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. (B) Western blot analysis showing cyclin B1 and p21 levels in p21 immunoprecipitates. (C) Western blot analysis cyclin B1 immunoprecipitates isolated from mock-treated (-) and p21-depleted cell extracts prepared from the same experiment. Numbers 1, 2, and 3 indicate differentially phosphorylated Cdk1 isoforms. Note that even in untreated E7 cells, a large population of cyclin B1-Cdk1 is bound to p21. In this immunoblot, the cyclin B1 signal (arrow) is obscured by a parasite background band. (D) Histone H1 kinase assays and Western blot analysis of cyclin B1 immunoprecipitates isolated from wild-type NHF synchronized in S, G2/M, and M (+ nocodazole) phases. Numbers 1, 2 and 3 indicate differentially phosphorylated Cdk1 isoforms, whereas the arrow points at the hypophosphorylated and active Cdk1. (E) Western blot analysis comparing cyclin B1 IP isolated from ICRF-193-treated E6 and E7 cultures. Numbers 1, 2, and 3 indicate differentially phosphorylated Cdk1 isoforms. To assess the phosphorylation status of the Cdk1 isoform 1 that accumulates in cyclin B1 IP in ICRF-193-treated E7 cells, immunoblots were probed with an antibody specific for CAK-phosphorylated phospho-threonine 161 (T161-P).