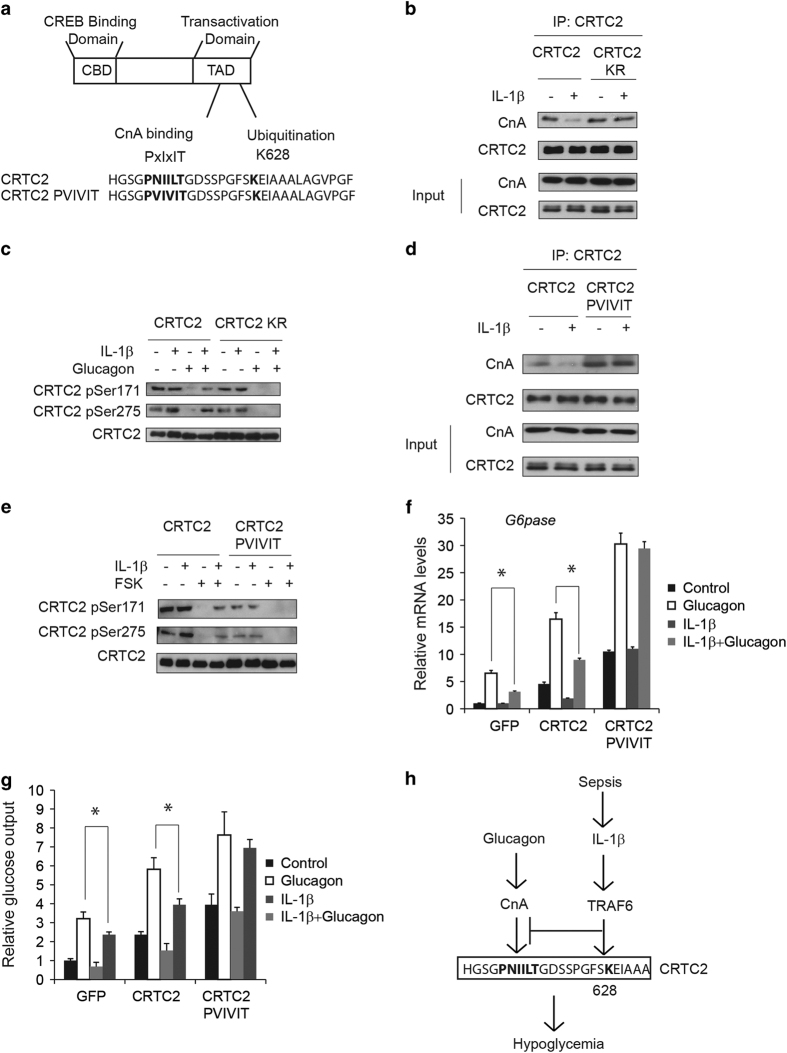
Figure 5.
TRAF6-mediated ubiquitination of CRTC2 disrupts its dephosphorylation via CnA. (a) Diagram and sequence of CRTC2 CnA-binding sites and ubiquitination site. (b) Effect of IL-1β (10 μg l−1) on CnA binding of wild type or K628R mutant CRTC2. (c) Effect of IL-1β (10 μg l−1) on dephosphorylation of wild type or K628R mutant CRTC2 in primary hepatocytes exposed to glucagon (20 nm). (d) Effect of IL-1β (10 μg l−1) on CnA binding of wild-type CRTC2 or mutant CRTC2 containing a high affinity CnA-binding site (PVIVIT). (e) Effect of IL-1β (10 μg l−1) on dephosphorylation of wild type or PVIVIT CRTC2 in primary hepatocytes exposed to glucagon (20 nm). (f, g) Effect of wild type and PVIVIT CRTC2 on G6pase mRNA amounts (f) and glucose output (g) in hepatocytes exposed to IL-1β (10 μg l−1) and glucagon (20 nm) (*P<0.05). (h) Schematic of proposed mechanism. In response to septic shock, pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β stimulates CRTC2 ubiquitination at Lys628 through TRAF6, which in turn blocks CRTC2 activation by disrupting CnA binding.