Figure 1.
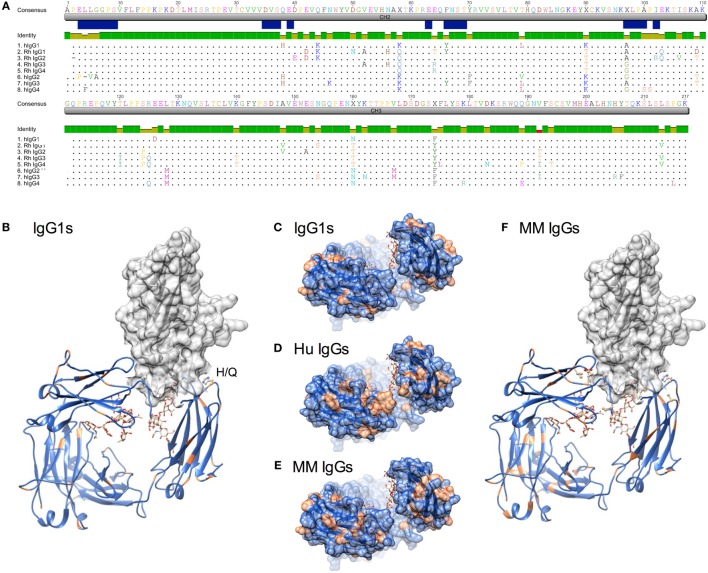
Sequence and structural differences between human and Macaca mulatta (MM) immunoglobulin G (IgG). (A) Sequence alignment of human IgG subclasses with the recombinant monoclonal rhesus macaque IgG. CH2 and CH3 domains are denoted in gray, whereas the N-linked glycosylation site and known human IgG Fc gamma receptors (FcγR) contact residues (35–38) are annotated in blue. (B) Structural model of human IgG1 CH2 and CH3 domains (ribbon) in complex with human FcγRIIIa extracellular domain (space-fill) in which amino acids that differ between rhesus and human IgG1 sequences for each species are colored orange (pdb 1T89). H38Q and oligosaccharides at N297 are illustrated in ball and stick. (C–E). A top-down view of the FcγR binding site, in which conserved positions are colored blue and variant positions colored orange. Oligosaccharides at N297 are illustrated in ball and stick. (C) Positional variance in the FcγR contact interface between human and MM IgG1. (D) Positional variance in the FcγR contact interface among the human IgG subclasses. (E) Positional variance in the FcγR contact interface among MM IgG subclasses. (F) Structural model of human IgG1 (ribbon) in complex with human FcγRIIIa (space-fill) in which amino acids that differ between MM IgG subclasses are colored orange. H38Q is illustrated in ball and stick.