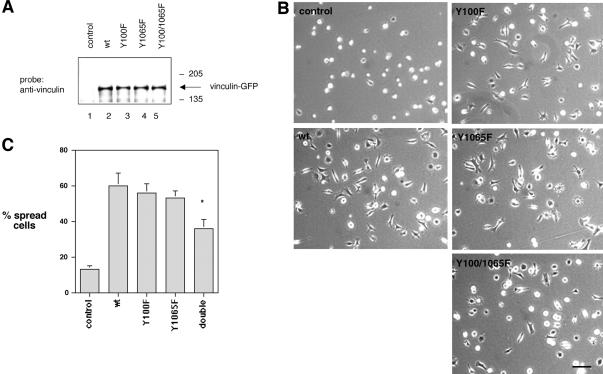
Figure 11.
Effect of wild-type and vinculin mutant proteins on cell spreading. Vinculin null cells were transfected with a cDNA encoding a puromycin resistant gene alone (control) or were cotransfected with cDNAs encoding for wild-type vinculin (wt) or the vinculin mutant proteins Y100F, Y1065F, or Y100F/Y1065F. (A) Lysates of puromycin resistant cultures were probed on Western blots with the mAb to vinculin. (B) Puromycin-resistant cells were allowed to spread on fibronectin-coated surfaces (10 μg/ml) for 2 h. The cells were fixed and examined by light microscopy. The images shown are representative of each cell population. Bar, 40 μm. (C) Cells in six random microscopic fields were scored as either spread or round for each population. The number of spread cells was expressed as a percentage relative to the total number of cells per field. Each data point represents the average ± SD of six fields. Approximately 500 cells were examined for each population in each experiment. Results are representative of three experiments. The difference in spreading between cells expressing the double mutant protein Y100F/Y1065F compared with cells expressing wt, Y100F, or Y1065F vinculin proteins was statistically significant (p ≤ 0.001) for all three comparisons.