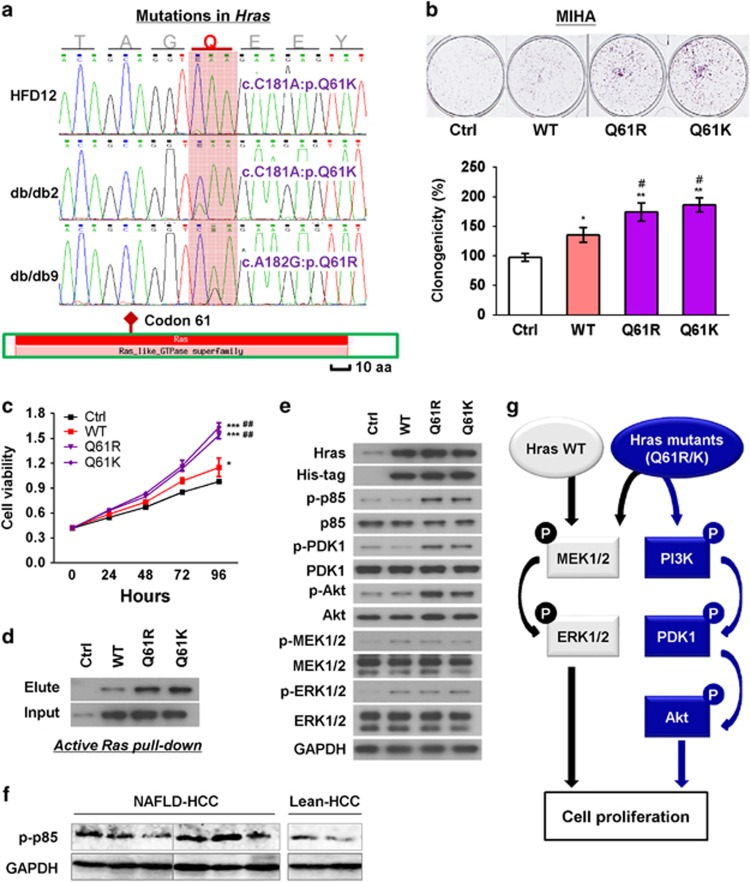
Figure 5.
Hras mutants promoted cell proliferation. (a) Somatic non-synonymous mutations in Hras (all located at codon 61) were found in NAFLD-HCCs of one dietary and two genetically obese mice but in none of the control lean mice. (b) Hras mutants (Q61R and Q61K) promoted cell proliferation compared with wild-type (WT) Hras and control vector (Ctrl) transfection in MIHA cells by colony formation assay. (c) Hras mutants (Q61R and Q61K) promoted cell viability compared with WT Hras and control vector transfection in MIHA cells by MTT assay. (d) Mutations of Q61R or Q61K enhanced the Ras activity of Hras. (e) Hras mutants (Q61R and Q61K) increased the protein expression of key regulators of Ras/MAPK and PI3K/AKT signaling cascades. (f) Protein level of p-p85 was examined by western blot in NAFLD-HCC and lean HCC from mouse models. The same bands for GAPDH were shown as in Figure 4e2 for the same protein samples. (g) Mechanistic scheme of signaling cascade mediated by wild-type and mutant Hras. Data were expressed as mean±s.d. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 as compared with control vector transfection; #P<0.05 and ##P<0.01 as compared with wild-type Hras.