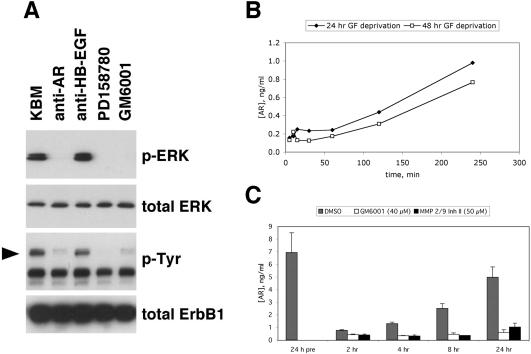
Figure 8.
Autocrine ERK phosphorylation in NHKs is dependent upon AR. (A) Neutralization experiments. GF-depleted NHKs were preincubated in fresh M154 medium for 120 min at 37°C with neutralizing antibodies against AR (5 μg/ml) or HB-EGF (5 μg/ml), or with PD158780 (1 μM) or GM6001 (40 μM). After lysate preparation and Western blotting (20 μg protein/lane), replicate blots were decorated with the antibodies indicated to the right of the autoradiograms. The result shown is from a single experiment and is representative of six experiments. The arrowhead indicates the mobility of ErbB1 (170–180 kDa). (B) Time course of AR accumulation. After GF deprivation in basal M154 for 24 h (closed diamonds) or 48 h (open squares), the medium was changed to fresh basal M154 and CM was collected and assayed for AR by ELISA. Data points represent the average of the two experiments, each of which was performed in duplicate. Note that accumulation of AR in the CM parallels the reappearance of ERK phosphorylation shown in Figure 1B. (C) MP inhibitors block production of soluble AR. NHKs (∼50% confluent) were deprived of growth factors in for 24 h in basal M154 medium, and aliquots of CM were collected. The medium was then changed to fresh basal M154 containing 40 μM GM6001, 50 μM MMP-2/9 inhibitor II, or 1:1000 (vol/vol) DMSO control. After time intervals varying from 2–24 h, aliquots of unconcentrated CM were assayed by ELISA as described in Materials and Methods. Error bars indicate SEM, n = 3–5, for all conditions except MMP-2/9 inhibitor II at 8 h, for which n = 2. p values were determined using a one-sided t test with unequal variances, with the null hypothesis being no reduction in AR by inhibitor at each time point. The nominal p value for the effect of this inhibitor versus DMSO control at this time point was 0.0056, all other nominal p values were <0.005. All p values remained significant at the p = 0.05 level after Bonferroni correction for eight tests.