Figure 2.
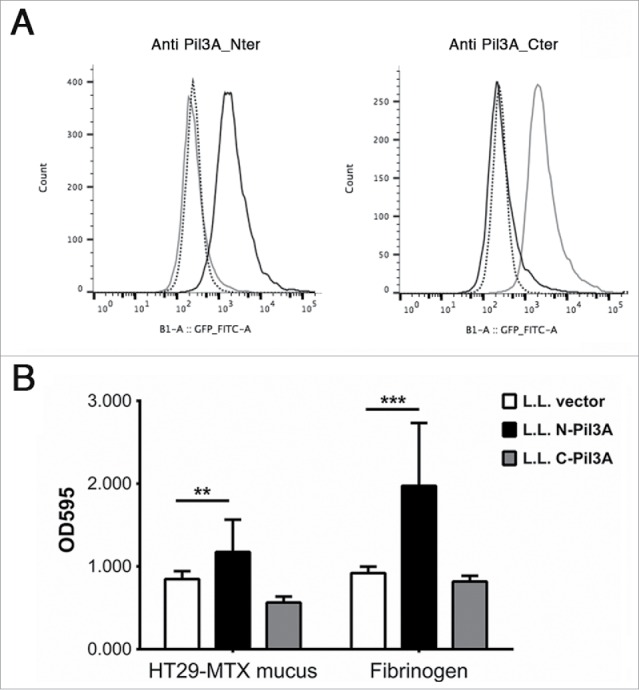
Adhesion of recombinant L. lactis expressing Pil3A to mucus and to fibrinogen. (A) Surface display of Pil3A-N (black line) or Pil3A-C (gray line) regions in recombinant L. lactis was determined by flow-cytometry using specific polyclonal antibodies directed against the amino- (Pil3A_Nter) or carboxyl- (Pil3A_Cter) part of Pil3A. The negative control (L. lactis carrying the empty vector) is shown in dotted line. In this representative experiment, 10,000 bacteria were analyzed for each strain. (B) Recombinant L. lactis strains expressing only the first 800 aa of Pil3A (N-Pil3A) displays higher binding to human HT29-MTX mucus and to fibrinogen as compared to the respective controls harboring the empty vector. Values indicate the mean of 3 independent experiments assayed in triplicate. Statistical analysis was performed using a 2-way ANOVA test (** p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001).
