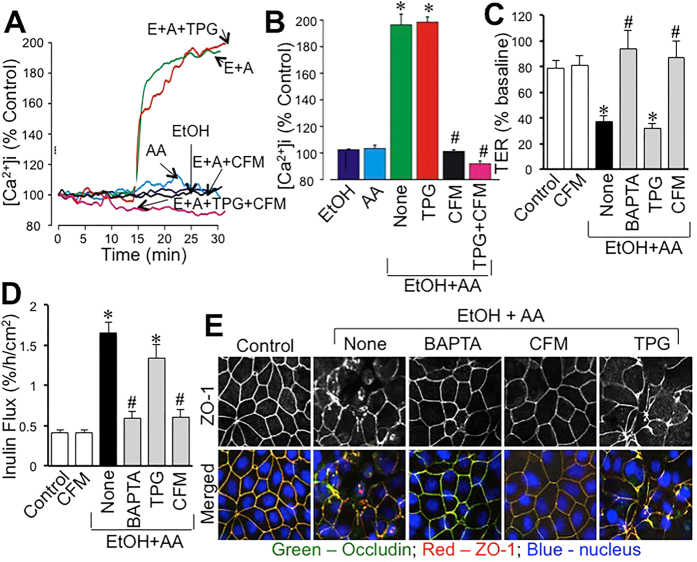
Figure 4. Synergistic elevation of intracellular Ca2+ by ethanol and acetaldehyde mediates tight junction disruption.
(A,B) Fura-2 loaded Caco-2 cell monolayers were incubated with 75 mM ethanol (EtOH), 200 μM acetaldehyde (AA) or acetaldehyde (200 μM) added 10 min after 75 mM ethanol (E+A) in the absence or presence of thapsigargin (TPG) or Ca2+-free medium (CFM). Real-time change in [Ca2+]i was measured and quantitated. Values are mean ± SEM (n = 10). Asterisks indicate the values that are significantly (p < 0.05) different from corresponding basal values; hash tags indicate values that are significantly (p < 0.05) different from value for E+A group. (C–E) Caco-2 cell monolayers were incubated with acetaldehyde (200 μM) added 10 min after 75 mM ethanol (EtOH+AA) in the absence (●) or presence of BAPTA-AM, TG, or CFM. Control cell monolayers received no treatments. TER (C) and inulin permeability (D) were measured after 4-hour incubation. Values are mean ± SEM (n = 8). Asterisks indicate the values that are significantly different (p < 0.05) from corresponding control values; hash tags indicate values that are significantly (p < 0.05) different from value for “None” group (●). Cell monolayers were fixed and stained for occludin and ZO-1 (E).