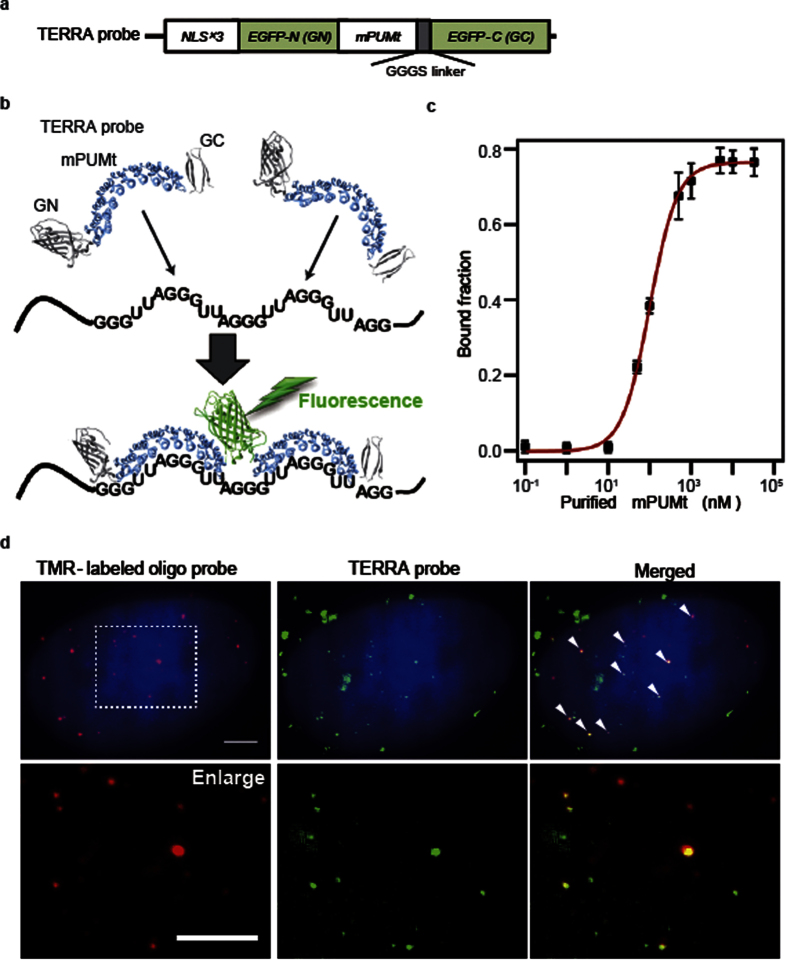
Figure 1.
Design and characterization of the TERRA probe: (a) Schematic of the domain structure of the TERRA probe. The mutant PUM-HD that binds to the repetitive RNA sequence (mPUMt) is sandwiched between split fragments of EGFP (N-terminal fragment: EGFP-N, C-terminal fragment: EGFP-C). The construct contains three tandem repeats of a NLS (NLS × 3). (b) Mechanism used to visualize TERRA with the probe. Binding of TERRA probes to the repeated target sequence induces intermolecular reconstitution of EGFP fragments, which recovers EGFP fluorescence. (c) Plot of RNA-bound fraction against mPUMt concentrations. (d) Localization of TERRA and TERRA probes. TERRA labeled with TMR-oligonucleotide (left) and the reconstituted EGFP on the TERRA probe (right) in the same cell. The white arrowheads in the merged image (right) show probes colocalized with TERRA. Bottom panels show enlarged images of the regions indicated by white dashed lines. Scale bar, 5.0 μm.