Fig. 1.
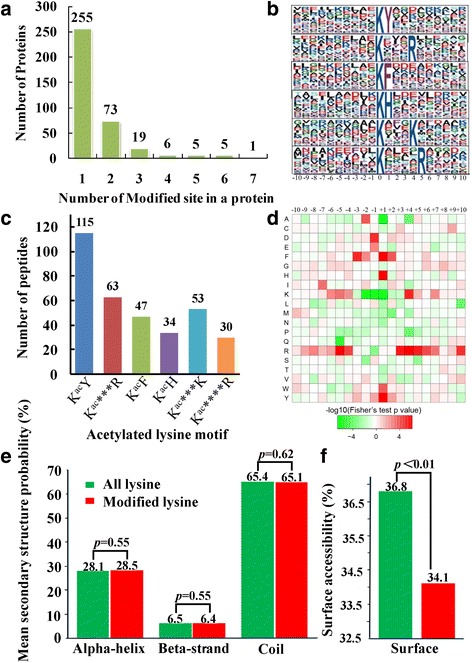
Properties of the acetylated sites. a Distribution of acetylated proteins based on their number of acetylation sites. Numbers of proteins with different acetylation sites (1–7) were shown on top of the columns. b Acetylation motifs and conservation of acetylation sites. The size of each letter corresponds to the frequency of the amino acid residue in that position. The central K refers to the acetylated lysine. c Distribution of identified proteins based on the acetylation motifs. Numbers of peptides with different conserved motifs were shown on top of the columns. d Heat map of the amino acid compositions of the acetylation sites showing the frequency of different amino acids around the acetylated lysine. Red indicates high frequency and green means low frequency. e Probabilities of lysine acetylation in different protein secondary structures. Different secondary structures (alpha-helix, beta-strand and coil) of acetylated lysine residues identified in this study were compared with those of all lysine on all proteins. f Predicted surface accessibility of acetylated sites. Surface accessibility of the acetylated lysine sites was compared with that of all lysine
