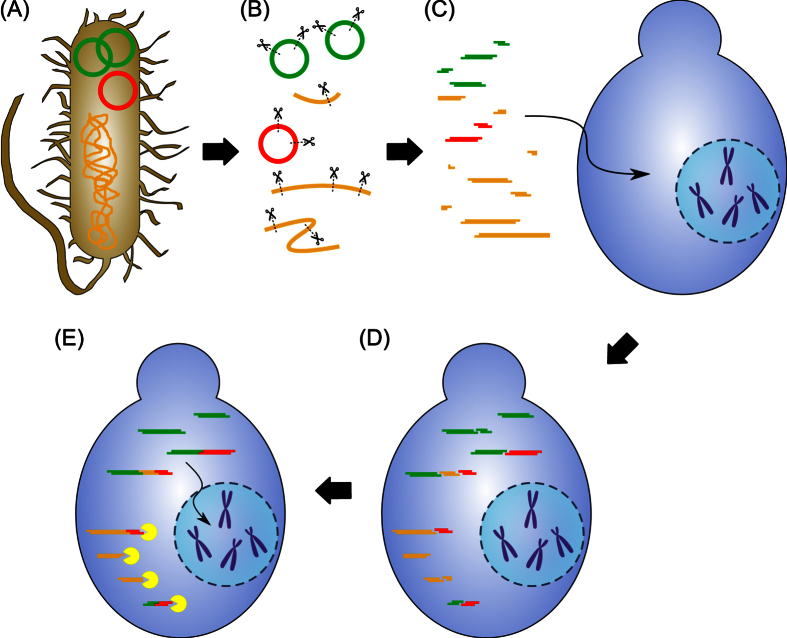
Figure 6. Schematic depiction of the proposed mechanism facilitating integration of E. coli host DNA in fusion with the expression cassette into the genome of P. pastoris.
(A) E. coli cells containing chromosomal (orange) and F plasmid (red) DNA are used to produce the expression vector (green) (B) During plasmid isolation F plasmids and fragmented chromosomal DNA are co-extracted with the expression vector. Subsequent enzymatic digestion creates compatible sticky ends (C) Restricted DNA is transferred into P. pastoris cells via e.g. electroporation (D) in vivo various fragment combinations are ligated and form new hybrids (E) Expression cassettes and hybrids containing expression cassettes with homologies to chromosomal loci of P. pastoris are integrated into the genome, while non-homologous DNA is degraded.