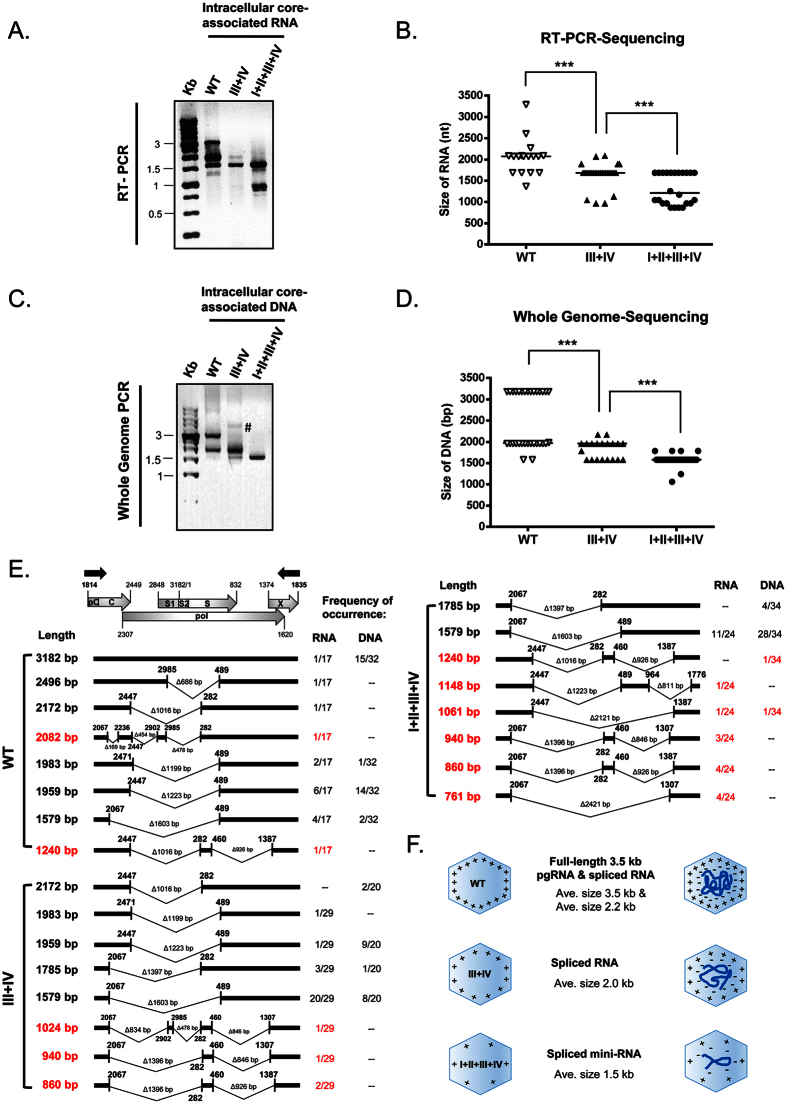
Figure 2. Arginine-deficient HBc mutants preferentially encapsidated spliced viral RNA and DNA.
(A) Core particle -associated viral RNAs of HBc ARD mutants were analyzed by RT-PCR and agarose gel with ethidium bromide staining. The positions of the RT-PCR primers are shown as black arrows in Fig. 2E. Compared to WT, mutant ARD-III + IV encapsidated shorter-sized viral RNAs, while mutant ARD-I + II + III + IV encapsidated the shortest RNA species. (B) The diagram summarized the statistics of RT-PCR sequencing results of core particle -associated viral RNAs of WT, mutants ARD-III + IV and I + II + III + IV. Each symbol represents one independently isolated clone from E. coli. The horizontal line represents the medium size of encapsidated RNA species. ***p < 0.001, by Student’s t-test. (C) Core particle-associated viral DNAs of HBc ARD mutants were analyzed by Whole Genome PCR and agarose gel with ethidium bromide staining. The positions of the Whole Genome PCR primers are near the triple-stranded DNA region (M&M10). Compared to WT, mutant ARD-III + IV encapsidated shorter -sized viral DNA, while mutant ARD-I + II + III + IV encapsidated the shortest-sized DNA. Symbol # marked a faint higher MW band which was not detected in other repeat experiments. (D) The diagram showed the statistics of PCR sequencing results of core particle-associated viral DNAs of WT, mutants ARD-III + IV and I + II + III + IV. Each symbol represents one independently isolated clone from E. coli. The horizontal line represents the medium size of encapsidated DNA species. ***p < 0.001, by Student’s t-test. (E) Sequencing results and frequencies of occurrence of each spliced species in E. coli clones from wild type and ARD mutants. A schematic representation of HBV pgRNA includes the pC (pre-core), C (core), pol (polymerase), S1/S2/S (surface proteins) and X (X protein). The red color represents novel spliced transcripts not reported previously in literature. (F) The cartoon highlights the trend of encapsidating smaller-sized RNA and DNA, when the arginine content at HBc ARD is reduced.