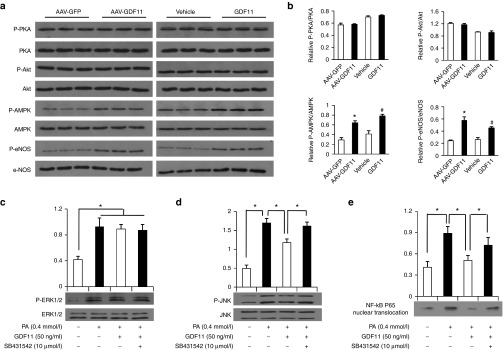
Figure 6.
GDF11 activated AMPK/eNOS signaling in vivo and inhibited inflammation signaling pathways in RAW264.7 macrophages. (a) Expression of PKA, P-PKA, Akt, P-Akt, AMPK, P-AMPK, eNOS, and P-eNOS in the aortas of apoE−/− mice were determined by western blot 12 weeks post AAV-GDF11 or others treatments. (b) Quantitative analysis of a. Data were shown as mean ± SD. Differences between two groups were tested with Student's t-test. n = 3 mice in each group. *P < 0.05 versus AAV-GFP; #P < 0.05 versus vehicle group. (c-e) Expression of ERK1/2, P-ERK1/2, JNK, P-JNK, and NF-κB P65 nuclear translocation levels in RAW264.7 macrophages were determined by western blot. Cells were pretreated with SB431542 for 30 minutes, and then treated with GDF11 (50 ng/ml) for 1 hour followed by stimulation with PA (0.4 mmol/l). Data were shown as mean ± SD. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by LSD t-test was used to compare the differences among different groups. Each experiment repeated five times. *P < 0.05. AAV, adeno-associated viruses; AAV-GFP, AAV-green fluorescent protein; GDF11, growth differentiation factor 11; SD, standard deviation; AMPK, adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; P-eNOS, phosphorylated endothelial nitricoxide synthase; ERK1/2, extracellular signal-regulated kinase1/2; JNK. c-jun N-terminal kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; LSD, least significant difference; PA, palmitic acid.