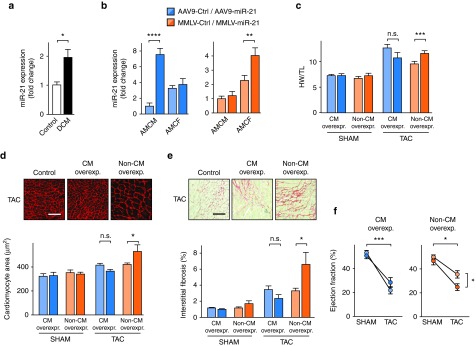
Figure 4.
Elevated expression of miR-21 in cardiac fibroblasts (CF) and endothelial cells exacerbates cardiac remodeling and is detrimental to cardiac function. (a) Quantification of miR-21 in human left ventricular myocardium from healthy and patients suffering from dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM). n = 5 per group. (b) Quantification of miR-21 in adult mouse cardiac myocytes (AMCM) and fibroblasts (AMCF) 5 weeks after infecting mice with miR-21-encoding AAV9 or MMLV, showing specific vector-dependent overexpression. Corresponding control vectors encoded the nonrelated C. elegans miR-39. (c) Ratio of heart weight to tibia length (HW/TL) from mice 4 weeks after TAC or sham surgery. (d) Wheat germ agglutinin staining in representative myocardial sections. (e) Representative Sirius red/Fast green staining of myocardial sections from the above mice (left), and quantitative data (right). (f) Echocardiographic determination of left ventricular ejection fraction in the above mice. Scale bars: 50 µm d and e. AAV9-Ctrl /-miR-21 Sham n = 4; TAC n = 6–7. MMLV-Ctrl/-miR-21 Sham n = 6–7; TAC n = 9. Data are mean ± SEM and were analyzed using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Sidak's post-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001. AAV9, adenoassociated virus of serotype 9; MMLV, moloney murine leukemia virus; TAC, transverse aortic constriction.