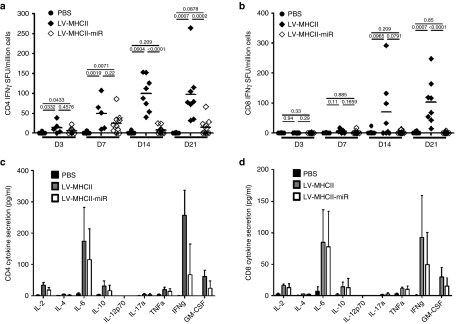
Figure 4.
LV-MHCII-miR vectors induce lower CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses than LV-MHCII vectors. C57Bl/6 female mice were intravenously (IV) injected in the tail vein with PBS, LV-MHCII or LV-MHCII-miR vectors. Immune responses were measured by interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot (ELISPOT) following a 24-hours-Dby or Uty ex vivo stimulation of splenocytes (a,b) or cytometric bead array (c,d). (a,b) Kinetics of response to 50 ng reverse transcriptase (RT) of vector. Immune response to LV-MHCII (a) or LV-MHCII-miR (b) was measured by IFN-γ ELISPOT 3, 7, 14, and 21 days after injection and following Dby or Uty peptide stimulation as indicated (n = 2 separate experiments, 5–10 mice per group). (c,d) Cytokine secreted following immunization. C57Bl/6 female mice were injected IV with PBS, 50 ng RT of LV-VSVg-GFP-HY or LV-MHCII vectors. After 7 days, spleen cells of these mice were harvested and assayed for IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, IL-17A, IFN-γ, TNFα, and GM-CSF secretion after 48 hours stimulation ex vivo with Dby (c) or Uty (d) using the cytometric bead array (n = 5 mice per group). GM-CSF, Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; GFP, green fluorescent protein; IL, interleukein; LN, lymph node; LV, lentiviral vectors; PBS, phosphate buffered saline; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor alpha.