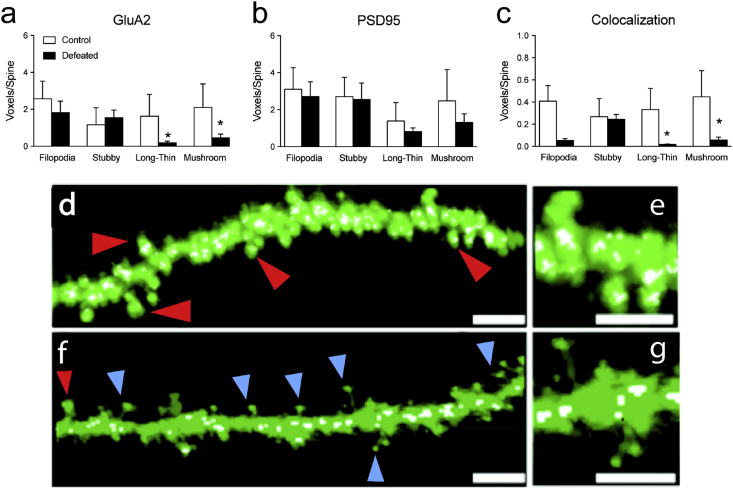
Fig. 5.
Effects of social stress on GluA2, PSD95, and their colocalization across spine types in the CA1 region of the hippocampus in adolescent C57BL/6 male mice. Social defeat stress decreased (a) GluA2 expression within long-thin and mushroom spines (*p < 0.05). (b) No changes in PSD95 were observed across spine types (p > 0.05) as a function of stress exposure. Conversely, (c) the number of spines expressing the colocalization of GluA2 and PSD95 was reduced in long-thin and mushroom spines (*p < 0.05). Representative images of a dendritic branch from a control (d–e) and socially defeated animal (f–g). Scale bar = 5 μm for d and f; 2.5 μm for e and g. Red arrows indicate stubby spines. Blue arrows indicate long-thin spines. White voxels represent GluA2/PSD95 colocalization. Data are represented as mean voxels per spine (mean + SEM). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)