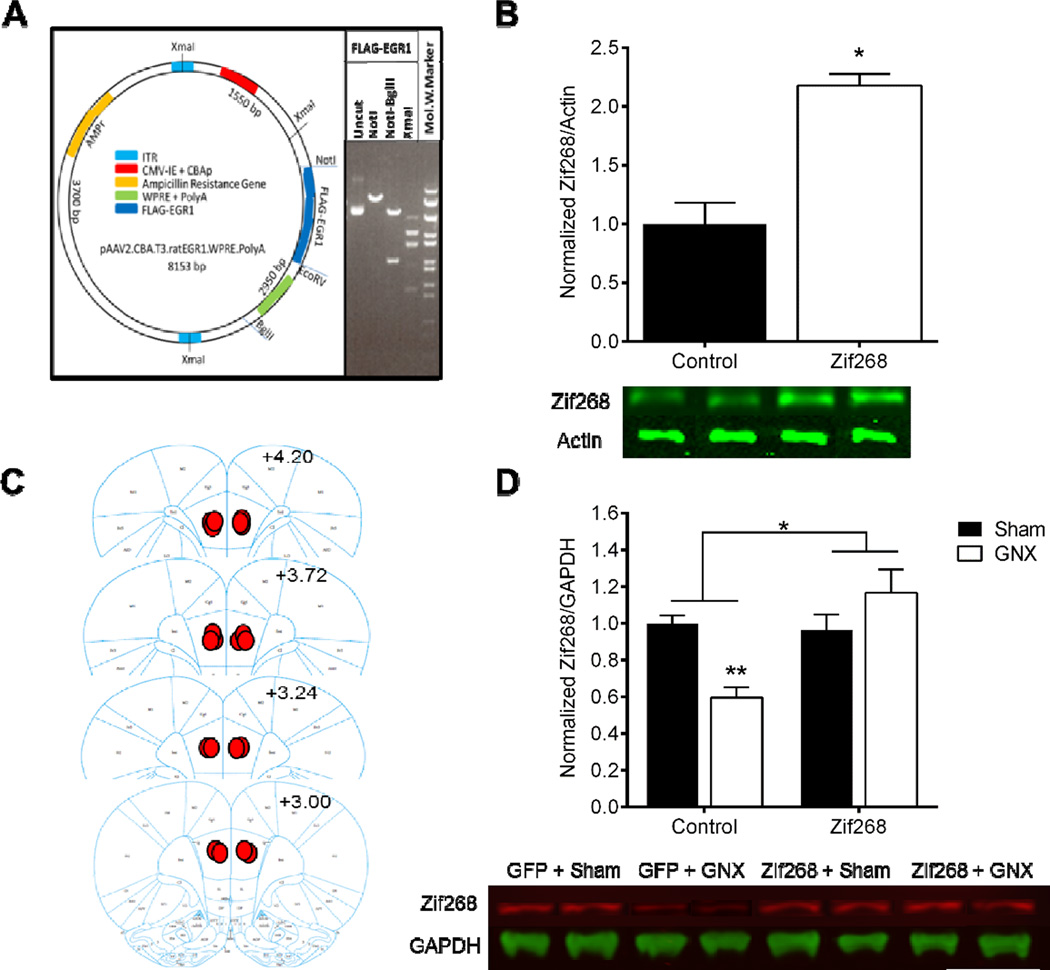
Figure 2. Delivery of AAV-Zif268 construct promotes overexpression of Zif268 in vitro and protects against GNX-induced mPFC Zif268 downregulation in vivo.
Map of the viral vector for AAV2.FLAG.EGR1 (Zif268) with the most relevant restriction sites and vector elements indicated and restriction enzyme digestion of uncut Zif268, cut with NotI, NotI + BglII, or XmaI (lanes 1, 2, 3, & 4, respectively) (A). Western blot analysis of HT22 cell lysates revealed that infection with AAV-Zif268 significantly increased amount of Zif268 as compared to the Control-treated cells (B). A diagram of representative medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) injection placements based on the atlas of Paxinos and Watson (2007); additional rats’ injections were identified at similar points between the anterior-posterior levels shown here (C). Western blot analysis confirmed GNX-induced down-regulation of Zif268 in the mPFC of animals that received Control virus; Zif268 protein expression was unchanged in Sham and GNX animals that received bilateral injection of AAV-Zif268 (D). Data are presented as means ± SEM. *p<0.05 Control versus AAV-Zif268, **p<0.05 versus all groups, n=2 plates/group in vitro, n=3–4/group in vivo.