Figure 2.
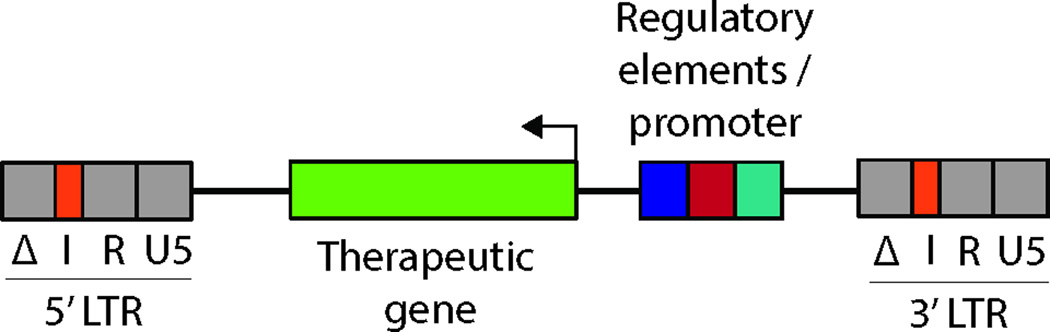
Simplified vector scheme illustrating a commonly used organization of a lentiviral vector for gene therapy. The vector contains the therapeutic gene of interest and transcriptional regulatory elements driving its expression. These elements are in reverse orientation with respect to viral transcription to avoid interference with viral processing, as is often the case in such vectors. The long terminal repeat region (LTR) is segmented into U3, R and U5 regions. For safety, the U3 repeat region is in a self-inactivating (SIN) configuration (Δ). An insulator element (I) has been introduced into the LTR to shield transcriptional effects of endogenous and exogenous chromatin elements after integration.
