Figure 3.
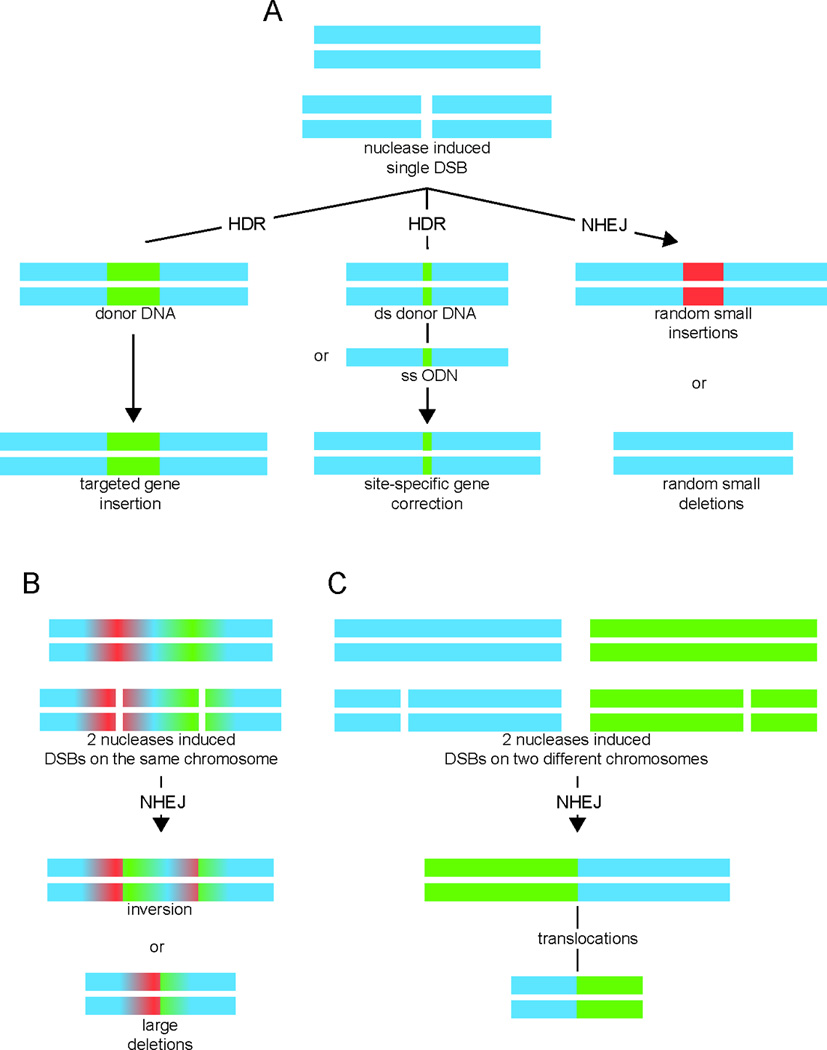
Nuclease-induced genome-editing. (A) Induction of a double strand break (DSB) by a nuclease either leads to non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) with indel formation (small random deletions or small random insertions), or results in homology-directed repair (HDR) after introduction of an either single-stranded oligodeoxynucleotide (ssODN) or a double-stranded donor DNA repair template containing the corrected sequence and flanking sequences that are homologous to the target locus. Alternatively, HDR may be utilized for targeted insertion of a gene, either at the endogenous locus or at a so-called safe harbor locus. (B) Induction of two DSBs by two nucleases on the same chromosome can result in inversion or large deletion of the flanking region. (C) Induction of two DSBs by two nucleases on different chromosomes may result in translocations. Figure has been modified from Kim and Kim [Kim and Kim, 2014].
