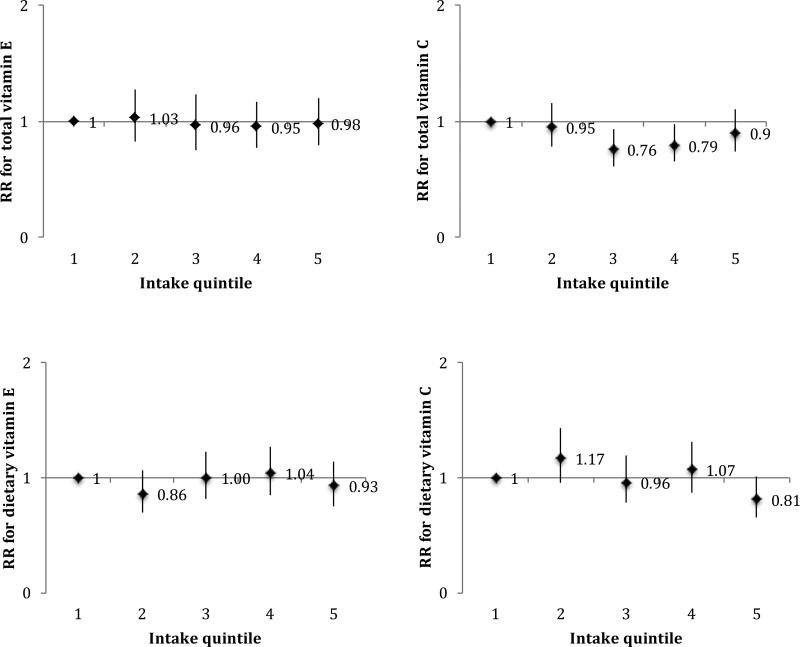
FIG. 1.
Associations of total and dietary vitamins E and C with PD according to intake quintiles, using cumulative average intake levels and adjusted for pack years of smoking, coffee intake, body mass index, physical activity, alcohol intake, and total energy intake. Median intake levels for each quintile of nutrients at baseline were as follows: for total vitamin E 6.0, 7.6, 9.3, 14.6, and 176.8 IU/day among women and 7.6, 9.6, 11.8, 18.8, and 193.6 IU/day among men; for total vitamin C 79, 130, 183, 302, and 825 mg/day among women and 95, 157, 228, 403, and 1159 mg/day among men; for dietary vitamin E 5.8, 6.8, 7.6, 8.5, and 10.2 IU/day among women, and 7.3, 8.7, 9.8, 11.1, and 13.7 IU/day among men; and for dietary vitamin C 67, 101, 128, 158, and 215 mg/day among women, and 78, 121, 154, 193, and 267 mg/day among men.