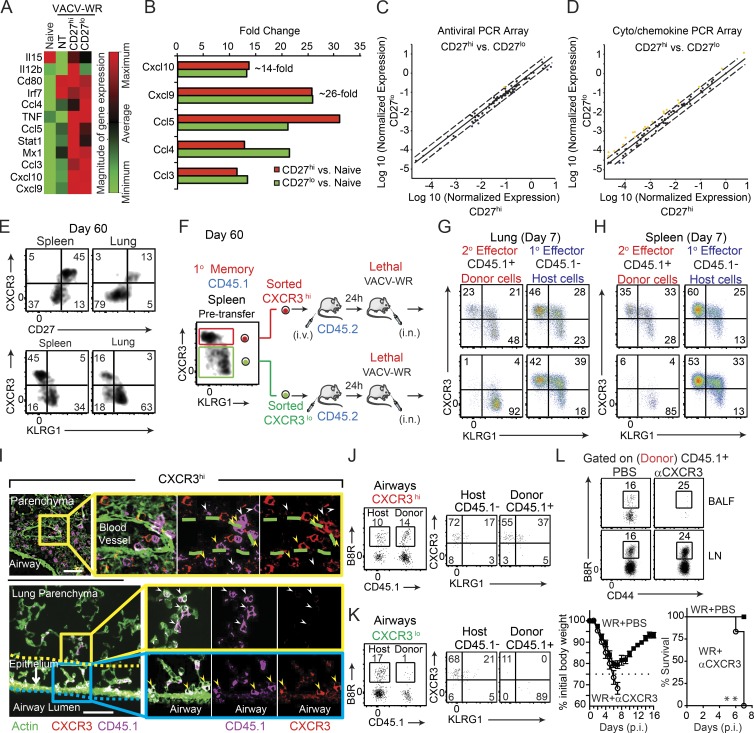
Figure 4.
CD27lo effector cells are directly generated from CD27hi memory populations, and CXCR3 expression determines their differential localization and protective value. (A–D) Mice that received CD8+CD44hi CD27hi and CD27lo memory T cells in Fig. 1 were analyzed on day 7 after infection. One group of B6 mice did not receive any memory cell and used as a NT control. Total lung mRNA transcript levels of 84 antiviral and cytokine/chemokine genes were measured and presented as a heat map (A). Fold change in gene expression between CD27hi recipients versus naive (B) CD27lo recipients versus naive (B) CD27hi versus CD27lo recipient mice (C and D) is also presented. All array data are presented as the mean of gene expression level of four animals per group. (E) Representative FACS plots depict CD27/CXCR3 (top) and CXCR3/KLRG1 (bottom) expression profiles gated on B8R20-27/Kb tetramer+ memory cells recovered from the spleen and lung 60 d after primary infection. Spleen memory cells were obtained as in Fig. 1 and sorted into CXCR3hiKLRGlo and CXCR3loKLRGhi and i.v. injected into B6 (CD45.2+) recipients that were lethally infected the next day with VACV-WR (F). Representative FACS plots depict CXCR3/KLRG1 profile of B8R20-27/Kb tetramer-specific donor (secondary [2°] effectors) and host (primary [1°] effectors) cells in lungs (G) and spleens (H) 7 d after infection. (I) IFA of lung sections from CXCR3hi-recipient mice were stained for CXCR3 (red), CD45.1 (magenta), and ActinGreen (green). Bars, 50 µm. The marked areas are shown in higher magnification to the right of each panel. Donor cells coexpressing CXCR3+ (red) and CD45.1+ (magenta) are indicated with yellow arrows, whereas donor CD45.1+ cells that down-regulated CXCR3 expression is delineated with white arrows. Endogenous cells could also be identified as only expressing CXCR3 (red only). Donor cells in close proximity to the airways epithelium are double positive. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from CXCR3hi (J) and CXCR3lo (K) recipient mice was harvested and stained for CD8α, CD44, KLRG1, CXCR3, CD45.1, and B8R20-27/Kb tetramer. (left) Representative FACS plots showing B8R20-27/Kb tetramer+ cells from the host (CD45.1−) and each of the transferred (CD45.1+) CXCR3hi (J) and CXCR3lo (K) populations as indicated. (right) Representative FACS plots for CXCR3/KLRG1 staining gated on CD8+CD44hiB8R20-27/Kb-tetramer+ are shown. Numbers indicate percentages of positive cells within the gated population. (L) 30,000 B8R-tetramer+ CD8+CD44hiCXCR3hi cells were i.v. transferred into naive (CD45.2+) recipient mice that were infected 1 d later with a lethal inoculum of VACV-WR. Infected mice were treated i.p. with PBS or mAb against CXCR3 on days 1, 3, and 5. Animals were analyzed on day 7. (top) Representative FACS plots showing B8R20-27/Kb tetramer+ cells gated on the transferred CD45.1+ cells. (bottom) Animals were weighed daily and euthanized if weight loss was >25% of initial body weight for two consecutive days. Mean percent of initial body weight is shown. Data are from one representative experiment of two with at least three mice per group (A–D and L) or at least three experiments with three and four mice per group (E–J). **, P < 0.01 (two-tailed Student’s t test or Mantel-Cox test used in L).