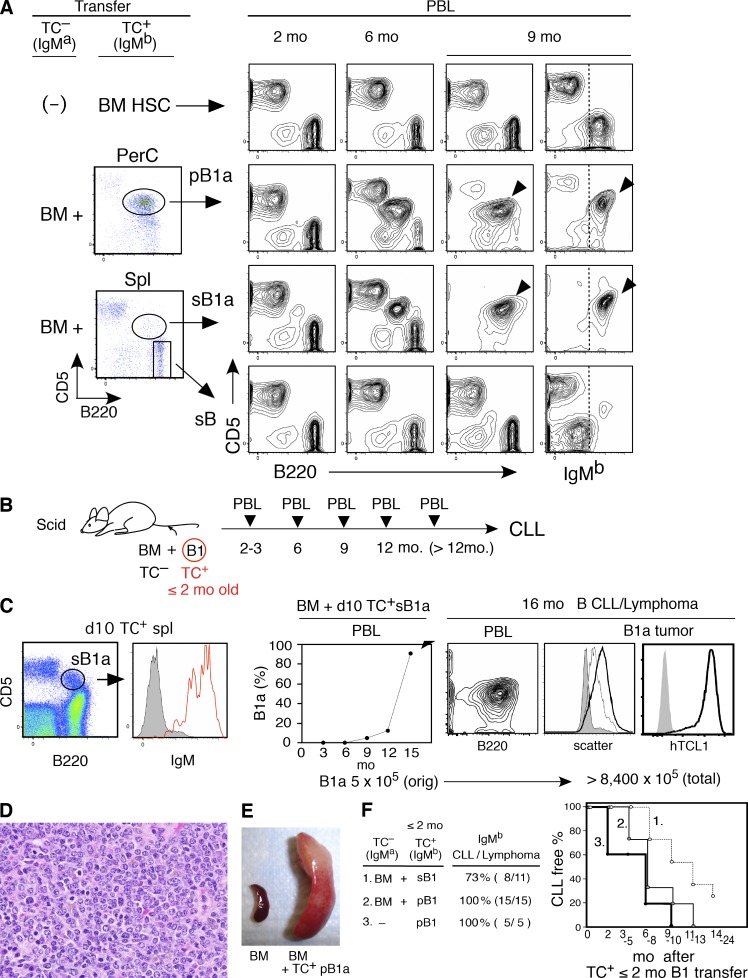
Figure 2.
CLL development from early generated B-1–derived B cells. (A) Comparison of CLL incidence in C.B17.scid recipients transferred with BM HSC, B1a, and non-B1a B cells purified from 2 mo TC+ C.B17 mice. pB1a and sB1a (each 5 × 105/recipient), and non-B1a spleen B cells (sB; 3 × 106/recipient) were cotransferred with TC– BALB/c BM. 2 mo after transfer, PBL showed similar numbers of B and T cells (top, using TC+ HSC alone were all IgMb, others were predominantly IgMa). Increase in B220loCD5+ B cells of IgMb B1a and CLL development are marked. PerC, peritoneal cavity. Representative of six transfer cases using 2–3-mo-old mice. TC+ mice together with TC– mice. (B) Cotransfer of purified B1 B cells from ≤2-mo-old TC+C.B17 mice with TC– BALB/c BM into C.B17.scid mice, monitoring PBL after transfer. (C) Transfer of B1a cells from 10-d-old TC+/− mice and development of CLL. 106 purified sB1a B cells (5 × 105 TC+) from 12 10-d-old (TC+/− x CB17)F1 mice were transferred together with 5 × 106 TC– BM cells into CB.17. mice. (left) Surface IgM expression of sB1a cells. (right) Frequency of B1a cells in PBL of recipient after adoptive transfer (middle). Characteristic mouse CLL CD5+B220+ phenotype and lymphomatous spleen B cells (thick black line) compared with original transferred B1a cells (thin black line and CD5−B220+ B cells (gray). Expression of hTCL1 Tg in this CLL is visualized by cytoplasmic staining (gray, second step control). Total leukemia B cell number indicated as a sum of IgMb+ B cells in PBL (2 × 108), spleen (4.6 × 108), and peritoneal cavity (1.8 × 108), as compared with the size of the initial TC+ inoculum. Representative of 15 cases with CLL/lymphoma generation by ≤2-mo-old mice. TC+ B1 B cell transfer. (D) H&E staining of spleen section with CLL/lymphoma of day 10 B1a cell origin. (E) Splenomegaly 8 mo after TC+ pB1a transferred together with TC– BM cells, compared with a recipient of TC– BM alone. (F) Summary of CLL/lymphoma incidence by purified B1 B cell transfer from ≤2-mo-old TC+ mice.