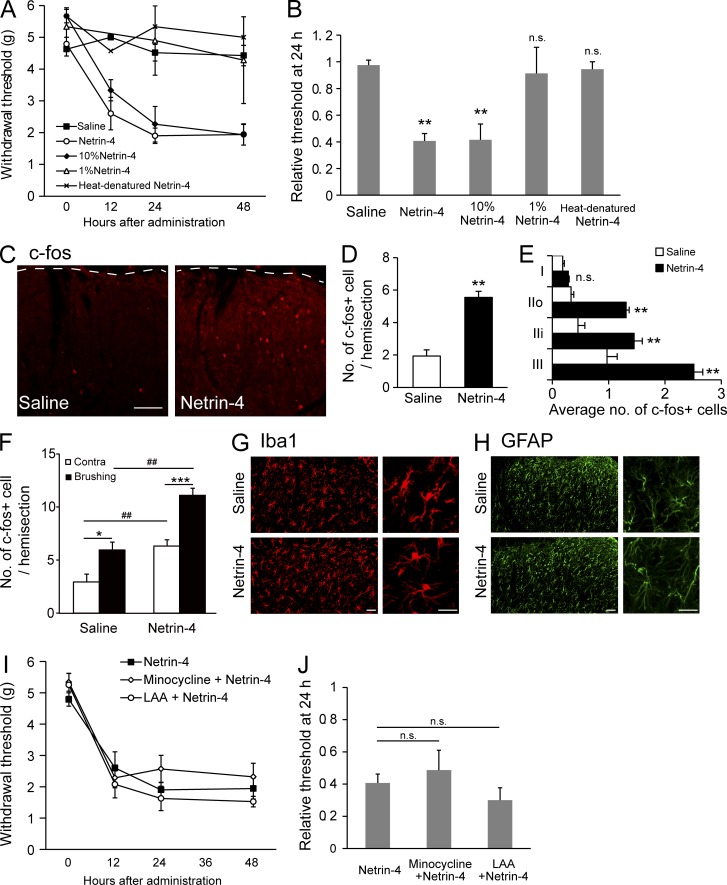
Figure 4.
Intrathecal administration of Netrin-4 induces tactile allodynia and neuronal activation. (A) Paw withdrawal thresholds after naive rats were treated with Netrin-4 (200 ng/d; ○; n = 11), 10% Netrin-4 (20 ng/d; ◆; n = 6), saline (■; n = 12), 1% Netrin-4 (2 ng/d; △; n = 4), or heat-denatured Netrin-4 (200 ng/d; ×; n = 6). (B) Thresholds at 24 h after administration were normalized to preadministration thresholds. (C) Immunofluorescence for c-fos in the L5 dorsal horn from the saline (left)- or Netrin-4 (right)–treated rats. The dashed lines represent the border between the gray and white matter in the lumbar cord. (D) The mean number of c-fos–expressing cells in 20-µm–thick hemisections from the L4-L5 dorsal horn. Data represent the mean from 4–6 rats. (E) Laminar distribution of c-fos–expressing cells in the superficial dorsal horn. (F) The mean number of c-fos–expressing cells in the L4-L5 dorsal horn of saline (n = 3)- or Netrin-4–administrated (n = 7) rats after brushing to the unilateral hind paw. Contra, contralateral. (G and H) Immunofluorescence of Iba1 (G) and GFAP (H) in saline- or Netrin-4–treated spinal cords. No obvious changes were noted in the morphology/cell number at 48 h after the administration of Netrin-4 (bottom) compared with the results from the saline-treated groups (top). (I) Paw withdrawal threshold after the administration of Netrin-4 (■; n = 6), minocycline with Netrin-4 (◇; n = 6), and l-a-aminoadipate (LAA) with Netrin-4 (○; n = 4). (J) Relative withdrawal thresholds at 24 h after administration. Bars: (C) 0.2 mm; (G and H) 50 µm. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ##, P < 0.01, versus saline-treated group; Tukey-Kramer test. Each experiment was performed three times in A–E and twice in F–J.