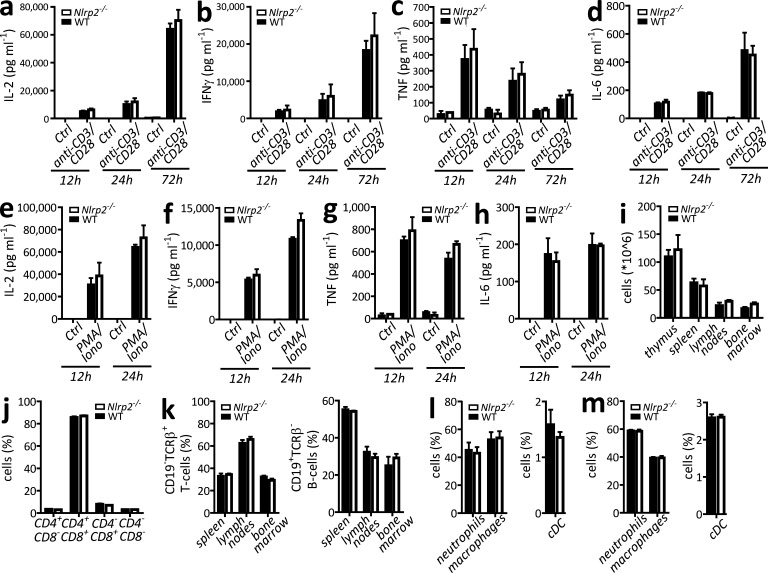
Figure 2.
CD4+ T cell responses are not modulated by Nlrp2 deficiency. (a–h) WT and Nlrp2−/− CD4+ T cells were left untreated or treated with anti-CD3 (4 µg ml−1; plate-bound) and anti-CD28 (1 µg ml−1) monoclonal antibodies (a–d), or treated with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA; 100 ng ml−1) and ionomycin (1 µg ml−1) for the indicated durations (e–h). Supernatants were analyzed for secretion of IL-2 (a and e), IFN-γ (b and f), TNF (c and g), and IL-6 (d and h). (i) Cellularity of primary and secondary immune organs of naive WT and Nlrp2−/− mice. (j) The fraction of immune cell subsets in thymus of naive WT and Nlrp2−/− mice was determined. Cells were defined as CD4+CD8−, CD4+CD8+, CD4−CD8+, or CD4−CD8−. (k) The fraction of CD19−TCRβ+ T (right) cells and CD19+TCRβ− B cells (left) in spleen, lymph nodes, and BM of naive WT and Nlrp2−/− mice was determined. (l) Myeloid cell subsets in spleen of naive WT and Nlrp2−/− mice were determined. Cells were gated as CD11b+CD11c−Gr1high neutrophils and CD11b+CD11c−Gr1low/neg macrophages (left), or as CD11b+CD11c+ conventional DCs (right). (m) Myeloid cell subsets in BM of naive WT and Nlrp2−/− mice were determined. Cells were gated as CD11b+CD11c−Gr1high neutrophils and CD11b+CD11c−Gr1low/neg macrophages (left), or as CD11b+CD11c+ conventional DCs (right). Analyses were performed on at least three mice/genotype. Data are representative of results from at least two independent experiments, and cytokine data are presented as mean ± SD from a single representative experiment, with each condition performed in triplicate. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t test; P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.