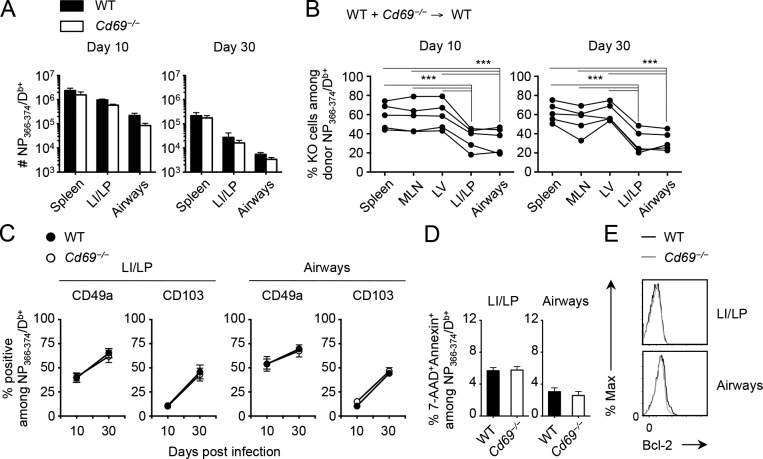
Figure 2.
Reduced accumulation of Cd69−/−/CD8+ T cells in the lung compared with CD69+/CD8+ T cells. (A) Numbers of NP-specific CD8+ T cells in each tissue of WT or Cd69−/− mice at day 10 and 30 after i.n. infection with x31. (B–E) Mice were treated with busulfan and 24 h later were injected with a 1:1 mixture of WT and Cd69−/− BM cells. 6 wk later, these mice were infected i.n. with x31. (B) Ratios of Cd69−/− cells among donor NP-specific CD8+ T cells in each tissue at day 10 and 30 PI. Lines connect data from each individual recipient mouse. (C) Ratios of CD49a+ and CD103+ cells among NP-specific CD8+ T cells in each tissue at the indicated time points. (D) Ratios of 7-AAD+annexin V+ cells among NP-specific CD8+ T cells in each tissue at day 30 PI. (E) Representative histograms showing Bcl-2 expression in WT (black lines) and Cd69−/− (gray lines) NP-specific CD8+ T cells in each tissue at day 30 PI. Data are representative of two independent experiments (mean and SEM of three to five mice per group). ***, P < 0.001 by two-way repeated measures ANOVA with Sidak’s posthoc tests (A and C), one-way repeated measures ANOVA with Tukey’s posthoc tests (B), and Student’s t test (D).